SNP-revealed genetic diversity in wild emmer wheat correlates with ecological factors
- PMID: 23937410
- PMCID: PMC3751623
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-13-169
SNP-revealed genetic diversity in wild emmer wheat correlates with ecological factors
Abstract
Background: Patterns of genetic diversity between and within natural plant populations and their driving forces are of great interest in evolutionary biology. However, few studies have been performed on the genetic structure and population divergence in wild emmer wheat using a large number of EST-related single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers.
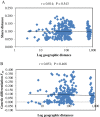
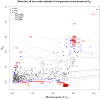
Results: In the present study, twenty-five natural wild emmer wheat populations representing a wide range of ecological conditions in Israel and Turkey were used. Genetic diversity and genetic structure were investigated using over 1,000 SNP markers. A moderate level of genetic diversity was detected due to the biallelic property of SNP markers. Clustering based on Bayesian model showed that grouping pattern is related to the geographical distribution of the wild emmer wheat. However, genetic differentiation between populations was not necessarily dependent on the geographical distances. A total of 33 outlier loci under positive selection were identified using a FST-outlier method. Significant correlations between loci and ecogeographical factors were observed.
Conclusions: Natural selection appears to play a major role in generating adaptive structures in wild emmer wheat. SNP markers are appropriate for detecting selectively-channeled adaptive genetic diversity in natural populations of wild emmer wheat. This adaptive genetic diversity is significantly associated with ecological factors.
Figures




References
-
- Nevo E, Korol AB, Beiles A, Fahima T. Evolution of wild emmer and wheat improvement: population genetics, genetic resources, and genome organization of wheat’s progenitor, Triticum dicoccoides. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2002.
-
- Peleg Z, Saranga Y, Krugman T, Abbo S, Nevo E, Fahima T. Allelic diversity associated with aridity gradient in wild emmer wheat populations. Plant Cell Environ. 2008;31:39–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

