WNK1-related Familial Hyperkalemic Hypertension results from an increased expression of L-WNK1 specifically in the distal nephron
- PMID: 23940364
- PMCID: PMC3761585
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1304230110
WNK1-related Familial Hyperkalemic Hypertension results from an increased expression of L-WNK1 specifically in the distal nephron
Abstract
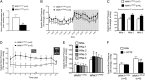
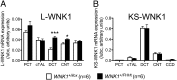
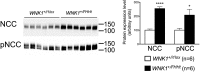
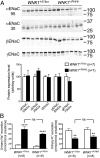
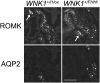
Large deletions in the first intron of the With No lysine (K) 1 (WNK1) gene are responsible for Familial Hyperkalemic Hypertension (FHHt), a rare form of human hypertension associated with hyperkalemia and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. We generated a mouse model of WNK1-associated FHHt to explore the consequences of this intronic deletion. WNK1(+/FHHt) mice display all clinical and biological signs of FHHt. This phenotype results from increased expression of long WNK1 (L-WNK1), the ubiquitous kinase isoform of WNK1, in the distal convoluted tubule, which in turn, stimulates the activity of the Na-Cl cotransporter. We also show that the activity of the epithelial sodium channel is not altered in FHHt mice, suggesting that other mechanisms are responsible for the hyperkalemia and acidosis in this model. Finally, we observe a decreased expression of the renal outer medullary potassium channel in the late distal convoluted tubule of WNK1(+/FHHt) mice, which could contribute to the hyperkalemia. In summary, our study provides insights into the in vivo mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of WNK1-mediated FHHt and further corroborates the importance of WNK1 in ion homeostasis and blood pressure.
Keywords: potassium balance; sodium transport; transgenic mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gordon RD, Hodsman GP. The syndrome of hypertension and hyperkalaemia without renal failure: Long term correction by thiazide diuretic. Scott Med J. 1986;31(1):43–44. - PubMed
-
- Schambelan M, Sebastian A, Rector FC., Jr Mineralocorticoid-resistant renal hyperkalemia without salt wasting (type II pseudohypoaldosteronism): Role of increased renal chloride reabsorption. Kidney Int. 1981;19(5):716–727. - PubMed
-
- Wilson FH, et al. Human hypertension caused by mutations in WNK kinases. Science. 2001;293(5532):1107–1112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

