Anatomic connections of the diaphragm: influence of respiration on the body system
- PMID: 23940419
- PMCID: PMC3731110
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S45443
Anatomic connections of the diaphragm: influence of respiration on the body system
Abstract
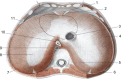
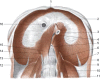
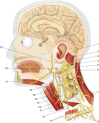
The article explains the scientific reasons for the diaphragm muscle being an important crossroads for information involving the entire body. The diaphragm muscle extends from the trigeminal system to the pelvic floor, passing from the thoracic diaphragm to the floor of the mouth. Like many structures in the human body, the diaphragm muscle has more than one function, and has links throughout the body, and provides the network necessary for breathing. To assess and treat this muscle effectively, it is necessary to be aware of its anatomic, fascial, and neurologic complexity in the control of breathing. The patient is never a symptom localized, but a system that adapts to a corporeal dysfunction.
Keywords: diaphragm; fascia; pelvis; phrenic nerve; vagus nerve.
Figures
References
-
- Downey R. Anatomy of the normal diaphragm. Thorac Surg Clin. 2011;21(2):273–279. - PubMed
-
- Anraku M, Shargall Y. Surgical conditions of the diaphragm: anatomy and physiology. Thorac Surg Clin. 2009;19(4):419–429. - PubMed
-
- Clugston RD, Greer JJ. Diaphragm development and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2007;16(2):94–100. - PubMed
-
- Arráez-Aybar LA, González-Gómez CC, Torres-García AJ, Morgagni-Larrey Parasternal diaphragmatic hernia in the adult. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2009;101(5):357–366. - PubMed
-
- Debergh I, Fierens K. Laparoscopic repair of a Bochdalek hernia with incarcerated bowel during pregnancy: report of a case. Surg Today. Jan 5, 2013. [Epub ahead of print.] - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

