MRI phantoms - are there alternatives to agar?
- PMID: 23940563
- PMCID: PMC3734012
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070343
MRI phantoms - are there alternatives to agar?
Abstract
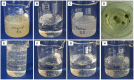
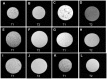
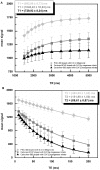
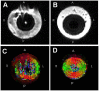
The suitability of different gelling agents as MRI phantoms was evaluated in terms of homogeneity, gel stability and reproducibility. Time and effort for preparation were also taken into account. The relaxation times of various gel compositions were estimated. Carbomer-980 and Carbopol-974P were determined to be promising novel phantom materials. These gelling agents are readily available, inexpensive and easy to handle given that thermal treatment is not required. Furthermore, the viscoelasticity of their polymer network is pH-dependent. With such characteristics, it was even possible to embed sensitive objects and retrieve them after testing. This was demonstrated with a fiber phantom for Diffusion Weighted MRI applications. Since Carbomer-980 and Carbopol-974P are non-hazardous, they are also suitable for multimodal setups (e.g., MRI as well as ultrasonic imaging).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

