Influence of a dopamine pathway additive genetic efficacy score on smoking cessation: results from two randomized clinical trials of bupropion
- PMID: 23941313
- PMCID: PMC3834197
- DOI: 10.1111/add.12325
Influence of a dopamine pathway additive genetic efficacy score on smoking cessation: results from two randomized clinical trials of bupropion
Abstract
Aims: To evaluate the associations of treatment and an additive genetic efficacy score (AGES) based on dopamine functional polymorphisms with time to first smoking lapse and point prevalence abstinence at end of treatment among participants enrolled into two randomized clinical trials of smoking cessation therapies.
Design: Double-blind pharmacogenetic efficacy trials randomizing participants to active or placebo bupropion. Study 1 also randomized participants to cognitive-behavioral smoking cessation treatment (CBT) or this treatment with CBT for depression. Study 2 provided standardized behavioural support.
Setting: Two hospital-affiliated clinics (study 1), and two university-affiliated clinics (study 2).
Participants: A total of 792 self-identified white treatment-seeking smokers aged ≥18 years smoking ≥10 cigarettes per day over the last year.
Measurements: Age, gender, Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence, dopamine pathway genotypes (rs1800497 [ANKK1 E713K], rs4680 [COMT V158M], DRD4 exon 3 variable number of tandem repeats polymorphism [DRD4 VNTR], SLC6A3,3' VNTR) analyzed both separately and as part of an AGES, time to first lapse and point prevalence abstinence at end of treatment.
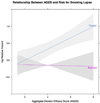
Findings: Significant associations of the AGES (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.10, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.06-1.14, P = 0.009) and of the DRD4 VNTR (HR = 1.29, 95% CI = 1.17-1.41, P = 0.0073) were observed with time to first lapse. A significant AGES by pharmacotherapy interaction was observed (β standard error = -0.18 [0.07], P = 0.016), such that AGES predicted risk for time to first lapse only for individuals randomized to placebo.
Conclusions: A score based on functional polymorphisms relating to dopamine pathways appears to predict lapse to smoking following a quit attempt, and the association is mitigated in smokers using bupropion.
Keywords: Bupropion; first lapse; genetic; pharmacogenetic analysis; randomized clinical trial.
© 2013 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Figures
References
-
- Jha P, Ramasundarahettige C, Landsman V, et al. 21st-century hazards of smoking and benefits of cessation in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:341–350. - PubMed
-
- Hughes JR, Stead LF, Lancaster T. Antidepressants for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007:CD000031. - PubMed
-
- Cahill K, Stead LF, Lancaster T. Nicotine receptor partial agonists for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;4:CD006103. - PubMed
-
- Stead LF, Perera R, Bullen C, et al. Nicotine replacement therapy for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;11:CD000146. - PubMed
-
- Stead LF, Lancaster T. Behavioural interventions as adjuncts to pharmacotherapy for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;12:CD009670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R24 GM061374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA084718/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-084718/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA084719/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-063532/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 GM061374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM-061374/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA027331/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA-020830/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- CA-084719/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-032318/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR000132/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA033813/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA025041/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA-017441/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA017441/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA-025041/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DA014276/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DA-027331/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA-014276/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DA020830/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous