Use of botulinum toxin in individuals with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: state of the art review
- PMID: 23941788
- PMCID: PMC3739890
- DOI: 10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000116
Use of botulinum toxin in individuals with neurogenic detrusor overactivity: state of the art review
Abstract
Background: Botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) injection into the bladder wall has been shown to be an effective alternative to anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) medications and more invasive surgery in those with multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury with neurogenic detrusor overactivity (NDO) and urinary incontinence who are not tolerating anticholinergic medications. In August 2011, Botox(®) (onabotulinumtoxinA) received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for this use. Clinically, intradetrusor injection of BoNT has been found to decrease urinary incontinence and improve quality of life. Its impact on urodynamic parameters is an increase in the maximum cystometric (bladder) capacity and decrease in the maximum detrusor pressures. The most common side effects are urinary tract infections and urinary retention. There have been rare reports and a black box warning of distant spread of BoNT. BoNT has gained popularity because of its effectiveness and long duration of action, relative ease of administration, easy learning curve, reproducibility of results on repeated administration, and low incidence of complications.
Objective: To discuss the structure and function, mechanisms of action, clinical and urodynamic studies, injection technique, potential beneficial and adverse effects, and potential areas of research of BoNT.
Methods: Literature search focused on botulinum toxin in MEDLINE/PubMed. Search terms included botulinum toxin, neurogenic bladder, NDO, botox bladder, botox spinal cord injury, botox, FDA, botox side effects. All papers identified were English language, full-text papers. In addition, English abstracts of non-English papers were noted. The reference list of identified articles was also searched for further papers.
Conclusion: Botulinum toxin is an alternative treatment for individuals with NDO who fail to tolerate anticholinergic medications. Its popularity has increased because of the literature, which has supported its effectiveness, safety, easy use and learning curve, reproducibility of results on repeated use, and recent FDA approval of Botox(®) (onabotulinumtoxinA).
Figures
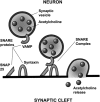
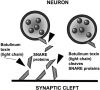
References
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardization Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn 2002;21(2):167–78 - PubMed
-
- Abrams P, Andersson KE, Birder L, Brubaker L, Cardoz L, Chapple C, et al. Fourth International Consultation on Incontinence Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and fecal incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn 2010;29(1):213–40 - PubMed
-
- Linsenmeyer TA. Neurogenic bladder following spinal cord injury. In: Kirshblum S, Campagnolo DI. (eds.) Spinal cord medicine. 2nd ed Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2011. p. 211–41
-
- Anderson KD, Borisoff JF, Johnson RD, Stiens SA, Elliott SL. The impact of spinal cord injury on sexual function: concerns of the general population. Spinal Cord 2007;45(5):328–37 - PubMed
-
- Coyne KS, Sexton CC, Irwin DE, Kopp ZS, Kelleher CJ, Milsom I. The impact of overactive bladder, incontinence and other lower urinary tract symptoms on quality of life, work productivity, sexuality and emotional well-being in men and women: results from the EPIC study. BJU Int 2008;101(11):1388–95 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
