Does hormone therapy affect blood pressure changes in the Diabetes Prevention Program?
- PMID: 23942251
- PMCID: PMC3858523
- DOI: 10.1097/GME.0b013e3182a0e3ea
Does hormone therapy affect blood pressure changes in the Diabetes Prevention Program?
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to examine whether blood pressure reductions differ by estrogen use among overweight glucose-intolerant women.
Methods: We conducted a secondary analysis of Diabetes Prevention Program postmenopausal participants who used oral estrogen with or without progestogen at baseline and 1-year follow-up (n = 324) versus those who did not use oral estrogen with or without progestogen at either time point (n = 382). Changes in systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were examined by randomization arm (intensive lifestyle change [ILS], metformin 850 mg twice daily, or placebo). Associations between changes in blood pressure and changes in sex hormone-binding globulin, estradiol, testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone were also examined.
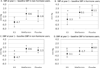
Results: Estrogen users and nonusers had similar prevalences of baseline hypertension (33% vs 34%, P = 0.82) and use of blood pressure medications at baseline (P = 0.25) and on follow-up (P = 0.10). Estrogen users and nonusers randomized to ILS had similar decreases in SBP (-3.3 vs -4.7 mm Hg, P = 0.45) and DBP (-3.1 vs -4.7 mm Hg, P = 0.16). Among estrogen users, women randomized to ILS had significant declines in SBP (P = 0.016) and DBP (P = 0.009) versus placebo. Among nonusers, women randomized to ILS had significant declines in DBP (P = 0.001) versus placebo, but declines in SBP were not significant (P = 0.11). Metformin was not associated with blood pressure reductions versus placebo regardless of estrogen therapy. Blood pressure changes were not associated with changes in sex hormones regardless of estrogen therapy.
Conclusions: Among overweight women with dysglycemia, the magnitude of blood pressure reductions after ILS is unrelated to postmenopausal estrogen use.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association of elective hormone therapy with changes in lipids among glucose intolerant postmenopausal women in the diabetes prevention program.Metabolism. 2013 Sep;62(9):1313-22. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 6. Metabolism. 2013. PMID: 23660512 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Racial/ethnic differences in sex hormone levels among postmenopausal women in the diabetes prevention program.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Nov;97(11):4051-60. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-2117. Epub 2012 Aug 9. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22879633 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sex hormone binding globulin and sex steroids among premenopausal women in the diabetes prevention program.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Jul;98(7):3049-57. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1341. Epub 2013 May 24. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 23709655 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reductions in glucose among postmenopausal women who use and do not use estrogen therapy.Menopause. 2013 Apr;20(4):393-400. doi: 10.1097/gme.0b013e3182703b73. Menopause. 2013. PMID: 23168523 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Smoking and Circulating Sex Hormone Levels Among Premenopausal Women.Nicotine Tob Res. 2022 Oct 26;24(11):1705-1713. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntac066. Nicotine Tob Res. 2022. PMID: 35291014
Cited by
-
Endogenous sex hormones, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes in men and women.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2014 Apr;16(4):467. doi: 10.1007/s11886-014-0467-6. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24585109 Free PMC article.
-
Confronting the challenges of the menopausal transition.Womens Midlife Health. 2015 Oct 5;1:7. doi: 10.1186/s40695-015-0008-5. eCollection 2015. Womens Midlife Health. 2015. PMID: 30766694 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Appel L, Champagne C, Harsha D, et al. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on blood pressure control: main results of the PREMIER clinical trial. JAMA. 2003;289:2083–2093. - PubMed
-
- Mulrow C, chiquette E, Angel L, et al. Dieting to reduce body weight for controlling hypertension in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;2:CD000484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK048406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK048489/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK083297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083297/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001449/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000041/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048489/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK071552/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK071552/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK084949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

