Inadequate testosterone suppression after medical and subsequent surgical castration in a patient with prostate cancer
- PMID: 23943809
- PMCID: PMC3761979
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-010395
Inadequate testosterone suppression after medical and subsequent surgical castration in a patient with prostate cancer
Abstract
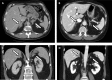
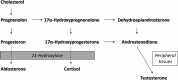
Androgen deprivation is a cornerstone in prostate cancer management. We present a 69-year-old man, with a poorly differentiated prostate cancer with skeletal and lymph node metastases. After medical and subsequent surgical castration serum testosterone concentrations remained inappropriately high (4.9 and 4.5 nmol/L; castration range < 0.5). For cancer staging a CT was performed which showed bilateral adrenal enlargement. Endocrine workup revealed elevated levels of adrenal androgens and adrenal precursors. Mutation analysis confirmed a non-classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency, that is, a mild form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH). To suppress adrenocorticotrophic hormone and the excess adrenal androgen secretion, treatment with hydrocortisone and prednisolone was started with success. Inadequate testosterone suppression after castration due to previously undiagnosed CAH has not previously been reported. Considering the estimated prevalence of 1% in selected populations, non-classical CAH should be considered when testosterone is not adequately suppressed after castration in men with prostate cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Thomas BC, Neal DE. Androgen deprivation treatment in prostate cancer. BMJ 2013;2013:e8555. - PubMed
-
- Immediate versus deferred treatment for advanced prostatic cancer: initial results of the Medical Research Council Trial. The Medical Research Council Prostate Cancer Working Party Investigators Group. Br J Urol 1997;2013:235–46 - PubMed
-
- Schulman CC, Irani J, Morote J, et al. Testosterone measurement in patients with prostate cancer. Eur Urol 2010;2013:65–74 - PubMed
-
- Crawford ED, Rove KO. Incomplete testosterone suppression in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2010;2013:1976. - PubMed
-
- Zlotta A, Debruyne F. Expert opinion on optimal testosterone control in prostate cancer. Eur Urol Suppl 2005;2013:37–41
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
