Five-year trends in antiretroviral usage and drug costs in HIV-infected children in Thailand
- PMID: 23945253
- PMCID: PMC3744770
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318298a309
Five-year trends in antiretroviral usage and drug costs in HIV-infected children in Thailand
Abstract
Background: As antiretroviral treatment (ART) programs mature, data on drug utilization and costs are needed to assess durability of treatments and inform program planning.
Methods: Children initiating ART were followed up in an observational cohort in Thailand. Treatment histories from 1999 to 2009 were reviewed. Treatment changes were categorized as: drug substitution (within class), switch across drug class (non nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI) to/from protease inhibitor (PI)), and to salvage therapy (dual PI or PI and NNRTI). Antiretroviral drug costs were calculated in 6-month cycles (US$ 2009 prices). Predictors of high drug cost including characteristics at start of ART (baseline), initial regimen, treatment change, and duration on ART were assessed using mixed-effects regression models.
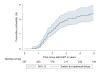
Results: Five hundred seven children initiated ART with a median 54 (interquartile range, 36-72) months of follow-up. Fifty-two percent had a drug substitution, 21% switched across class, and 2% to salvage therapy. When allowing for drug substitution, 78% remained on their initial regimen. Mean drug cost increased from $251 to $428 per child per year in the first and fifth year of therapy, respectively. PI-based and salvage regimens accounted for 16% and 2% of treatments prescribed and 33% and 5% of total costs, respectively. Predictors of high cost include baseline age ≥ 8 years, non nevirapine-based initial regimen, switch across drug class, and to salvage regimen (P < 0.005).
Conclusions: At 5 years, 21% of children switched across drug class and 2% received salvage therapy. The mean drug cost increased by 70%. Access to affordable second- and third-line drugs is essential for the sustainability of treatment programs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS. [Accessed 15th August 2012];Together we will end AIDS. 2012 http://www.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epidemiolo....
-
- Meyer-Rath G, Brennan A, Long L, et al. Cost and outcomes of paediatric antiretroviral treatment in South Africa. AIDS. 2012:e25–e32. Publish Ahead of Print. - PubMed
-
- Harling G, Wood R. The Evolving Cost of HIV in South Africa: Changes in Health Care Cost With Duration on Antiretroviral Therapy for Public Sector Patients. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2007;45(3):348–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous