Crucial role for early growth response-1 in the transcriptional regulation of miR-20b in breast cancer
- PMID: 23945289
- PMCID: PMC3824527
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1165
Crucial role for early growth response-1 in the transcriptional regulation of miR-20b in breast cancer
Abstract
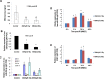
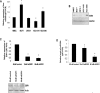
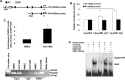
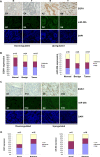
Transcriptional regulation of miRNAs that control the pathogenesis of breast cancer remains largely unknown. Here, we showed that ionizing radiation, a known breast carcinogen, triggered the differential expression of miR-20b in mammary tissues. We identified several GC-rich consensus binding motifs for the zinc finger transcription factor early growth response-1 (EGR1) in miR-20b promoter. miR-20b was upregulated by IR and its upregulation correlated with EGR1 expression in the breast cancer cell line HCC1806. Therefore, we used HCC1806 cells as a model system to explore the role of EGR1 in miR-20b transcription. siRNA knockdown of EGR1 attenuated miR-20b expression. Luciferase assays showed that whereas EGR1 stimulated luciferase activity driven by the wild-type miR-20b promoter, this induction was abolished in the mutant miR-20 promoter construct. We noted significant enrichment of EGR1 at miR-20b promoter in HCC1806 cells compared with normal human mammary epithelial cells. Suppression of miR-20b significantly inhibited HCC1806 cell proliferation and migration, and led to G0/G1 and S phase arrest. In vitro RNA-pull down assays indicated that miR-20b targets numerous tumor suppressors, including PTEN and BRCA1, which were downregulated in HCC1806. Conversely, suppression of miR-20b increased PTEN and BRCA1 levels. Moreover, immunohistochemical and FISH analyses showed that the miR-20b expression correlated significantly with EGR1 levels in breast cancer tissues. Our findings thus demonstrate for the first time that EGR1 is a key player in the transcriptional control of miR-20b, and miR-20b may in turn function as an oncogene by contributing to breast tumorigenesis via tumor suppressor targeting.
Figures



References
-
- Schairer C, Mink PJ, Carroll L, Devesa SS. Probabilities of death from breast cancer and other causes among female breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1311–21. - PubMed
-
- Mattsson A, Rudén BI, Hall P, Wilking N, Rutqvist LE. Radiation-induced breast cancer: Long-term follow-up of radiation therapy for benign breast disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:1679–85. - PubMed
-
- Doody MM, Lonstein JE, Stovall M, Hacker DG, Luckyanov N, Land CE. Breast cancer mortality after diagnostic radiography: findings from U.S. Scoliosis Cohort Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25:2052–63. - PubMed
-
- Stecklein SR, Jensen RA, Pal A. Genetic and epigenetic signatures of breast cancer subtypes. Front Biosci (Elite Ed) 2012;4:934–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

