Yeast ribosomal protein L7 and its homologue Rlp7 are simultaneously present at distinct sites on pre-60S ribosomal particles
- PMID: 23945946
- PMCID: PMC3814368
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt726
Yeast ribosomal protein L7 and its homologue Rlp7 are simultaneously present at distinct sites on pre-60S ribosomal particles
Abstract
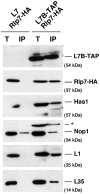
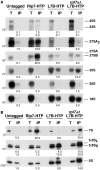
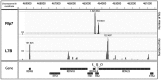
Ribosome biogenesis requires >300 assembly factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Ribosome assembly factors Imp3, Mrt4, Rlp7 and Rlp24 have sequence similarity to ribosomal proteins S9, P0, L7 and L24, suggesting that these pre-ribosomal factors could be placeholders that prevent premature assembly of the corresponding ribosomal proteins to nascent ribosomes. However, we found L7 to be a highly specific component of Rlp7-associated complexes, revealing that the two proteins can bind simultaneously to pre-ribosomal particles. Cross-linking and cDNA analysis experiments showed that Rlp7 binds to the ITS2 region of 27S pre-rRNAs, at two sites, in helix III and in a region adjacent to the pre-rRNA processing sites C1 and E. However, L7 binds to mature 25S and 5S rRNAs and cross-linked predominantly to helix ES7(L)b within 25S rRNA. Thus, despite their predicted structural similarity, our data show that Rlp7 and L7 clearly bind at different positions on the same pre-60S particles. Our results also suggest that Rlp7 facilitates the formation of the hairpin structure of ITS2 during 60S ribosomal subunit maturation.
Figures

References
-
- Kressler D, Hurt E, Bassler J. Driving ribosome assembly. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010;1803:673–683. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

