A dramatic increase of C1q protein in the CNS during normal aging
- PMID: 23946404
- PMCID: PMC3742932
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1333-13.2013
A dramatic increase of C1q protein in the CNS during normal aging
Abstract
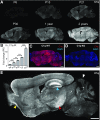
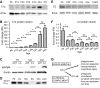
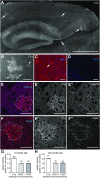
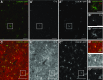
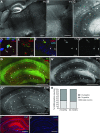
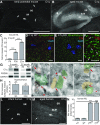
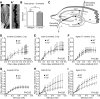
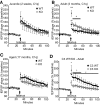
The decline of cognitive function has emerged as one of the greatest health threats of old age. Age-related cognitive decline is caused by an impacted neuronal circuitry, yet the molecular mechanisms responsible are unknown. C1q, the initiating protein of the classical complement cascade and powerful effector of the peripheral immune response, mediates synapse elimination in the developing CNS. Here we show that C1q protein levels dramatically increase in the normal aging mouse and human brain, by as much as 300-fold. This increase was predominantly localized in close proximity to synapses and occurred earliest and most dramatically in certain regions of the brain, including some but not all regions known to be selectively vulnerable in neurodegenerative diseases, i.e., the hippocampus, substantia nigra, and piriform cortex. C1q-deficient mice exhibited enhanced synaptic plasticity in the adult and reorganization of the circuitry in the aging hippocampal dentate gyrus. Moreover, aged C1q-deficient mice exhibited significantly less cognitive and memory decline in certain hippocampus-dependent behavior tests compared with their wild-type littermates. Unlike in the developing CNS, the complement cascade effector C3 was only present at very low levels in the adult and aging brain. In addition, the aging-dependent effect of C1q on the hippocampal circuitry was independent of C3 and unaccompanied by detectable synapse loss, providing evidence for a novel, complement- and synapse elimination-independent role for C1q in CNS aging.
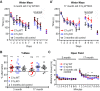
Figures
References
-
- Benoit ME, Hernandez MX, Dinh ML, Benavente F, Vasquez O, Tenner AJ. C1q-induced LRP1B and GPR6 proteins expressed early in Alzheimer disease mouse models, are essential for the C1q-mediated protection against amyloid-beta neurotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:654–665. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400168. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NS069375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS069375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH65541/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS059893/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA15403/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS059893/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- OD010927/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG000538/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH020016/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI041090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH065541/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AG00538/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K26 OD010927/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA015403/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AI41090/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
