Protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of Rap1 regulates its membrane localization and cell migration
- PMID: 23946483
- PMCID: PMC3784689
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.466904
Protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of Rap1 regulates its membrane localization and cell migration
Abstract
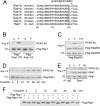
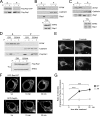
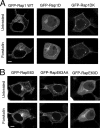
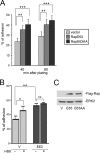
The small G protein Rap1 can mediate "inside-out signaling" by recruiting effectors to the plasma membrane that signal to pathways involved in cell adhesion and cell migration. This action relies on the membrane association of Rap1, which is dictated by post-translational prenylation as well as by a stretch of basic residues within its carboxyl terminus. One feature of this stretch of acidic residues is that it lies adjacent to a functional phosphorylation site for the cAMP-dependent protein kinase PKA. This phosphorylation has two effects on Rap1 action. One, it decreases the level of Rap1 activity as measured by GTP loading and the coupling of Rap1 to RapL, a Rap1 effector that couples Rap1 GTP loading to integrin activation. Two, it destabilizes the membrane localization of Rap1, promoting its translocation into the cytoplasm. These two actions, decreased GTP loading and decreased membrane localization, are related, as the translocation of Rap1-GTP into the cytoplasm is associated with its increased GTP hydrolysis and inactivation. The consequences of this phosphorylation in Rap1-dependent cell adhesion and cell migration were also examined. Active Rap1 mutants that lack this phosphorylation site had a minimal effect on cell adhesion but strongly reduced cell migration, when compared with an active Rap1 mutant that retained the phosphorylation site. This suggests that optimal cell migration is associated with cycles of Rap1 activation, membrane egress, and inactivation, and requires the regulated phosphorylation of Rap1 by PKA.
Keywords: Cell Adhesion; Cell Migration; Electrostatic Switch; Geranylgeranylation; Low Molecular Weight G Proteins; Phosphorylation; Protein Kinase A (PKA); Rap1; cAMP.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ubc9 Binds to ADAP and Is Required for Rap1 Membrane Recruitment, Rac1 Activation, and Integrin-Mediated T Cell Adhesion.J Immunol. 2017 Dec 15;199(12):4142-4154. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700572. Epub 2017 Nov 10. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29127148
-
Rap1-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by cyclic AMP is dependent on the mode of Rap1 activation.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Mar;26(6):2130-45. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.6.2130-2145.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16507992 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated regulation of Rap1 and thyroid differentiation by cyclic AMP and protein kinase A.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Mar;21(6):1921-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.6.1921-1929.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11238928 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of lymphocyte adhesion and migration by the small GTPase Rap1 and its effector molecule, RAPL.Immunol Lett. 2004 Apr 30;93(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2004.02.008. Immunol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15134891 Review.
-
The Many Faces of Rap1 GTPase.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 20;19(10):2848. doi: 10.3390/ijms19102848. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30241315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NADPH Oxidase Deficiency: A Multisystem Approach.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:4590127. doi: 10.1155/2017/4590127. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29430280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PP2Acα promotes macrophage accumulation and activation to exacerbate tubular cell death and kidney fibrosis through activating Rap1 and TNFα production.Cell Death Differ. 2021 Sep;28(9):2728-2744. doi: 10.1038/s41418-021-00780-5. Epub 2021 May 1. Cell Death Differ. 2021. PMID: 33934104 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 20;8(1):14098. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32539-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30237527 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal pattern and synergy influence activity of ERK signaling pathways during L-LTP induction.Elife. 2021 Aug 10;10:e64644. doi: 10.7554/eLife.64644. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34374340 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Rap1 by cAMP-dependent Protein Kinase (PKA) Creates a Binding Site for KSR to Sustain ERK Activation by cAMP.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jan 27;292(4):1449-1461. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.768986. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28003362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McLaughlin S., Aderem A. (1995) The myristoyl-electrostatic switch. A modulator of reversible protein-membrane interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 20, 272–276 - PubMed
-
- Roy M. O., Leventis R., Silvius J. R. (2000) Mutational and biochemical analysis of plasma membrane targeting mediated by the farnesylated, polybasic carboxy terminus of K-ras4B. Biochemistry 39, 8298–8307 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

