Widespread and enzyme-independent Nε-acetylation and Nε-succinylation of proteins in the chemical conditions of the mitochondrial matrix
- PMID: 23946487
- PMCID: PMC3790002
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.486753
Widespread and enzyme-independent Nε-acetylation and Nε-succinylation of proteins in the chemical conditions of the mitochondrial matrix
Abstract
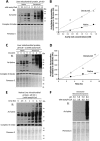
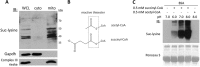
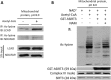
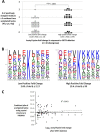
Alterations in mitochondrial protein acetylation are implicated in the pathophysiology of diabetes, the metabolic syndrome, mitochondrial disorders, and cancer. However, a viable mechanism responsible for the widespread acetylation in mitochondria remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that the physiologic pH and acyl-CoA concentrations of the mitochondrial matrix are sufficient to cause dose- and time-dependent, but enzyme-independent acetylation and succinylation of mitochondrial and nonmitochondrial proteins in vitro. These data suggest that protein acylation in mitochondria may be a chemical event facilitated by the alkaline pH and high concentrations of reactive acyl-CoAs present in the mitochondrial matrix. Although these results do not exclude the possibility of enzyme-mediated protein acylation in mitochondria, they demonstrate that such a mechanism may not be required in its unique chemical environment. These findings may have implications for the evolutionary roles that the mitochondria-localized SIRT3 deacetylase and SIRT5 desuccinylase have in the maintenance of metabolic health.
Keywords: Acetyl Coenzyme A; Acetylation; Metabolic Diseases; Metabolic Regulation; Mitochondrial Metabolism; Nonenzymatic; Sirtuins; Succinyl Coenzyme A; Succinylation; pH Regulation.
Figures



References
-
- Choudhary C., Kumar C., Gnad F., Nielsen M. L., Rehman M., Walther T. C., Olsen J. V., Mann M. (2009) Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 325, 834–840 - PubMed
-
- Strahl B. D., Allis C. D. (2000) The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403, 41–45 - PubMed
-
- Starai V. J., Celic I., Cole R. N., Boeke J. D., Escalante-Semerena J. C. (2002) Sir2-dependent activation of acetyl-CoA synthetase by deacetylation of active lysine. Science 298, 2390–2392 - PubMed
-
- Hebert A. S., Dittenhafer-Reed K. E., Yu W., Bailey D. J., Selen E. S., Boersma M. D., Carson J. J., Tonelli M., Balloon A. J., Higbee A. J., Westphall M. S., Pagliarini D. J., Prolla T. A., Assadi-Porter F., Roy S., Denu J. M., Coon J. J. (2013) Calorie restriction and SIRT3 trigger global reprogramming of the mitochondrial protein acetylome. Mol. Cell 49, 186–199 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

