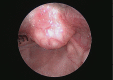
Vallecular cyst as a cause of obstructive sleep apnea in an infant
- PMID: 23946714
- PMCID: PMC3716675
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.2932
Vallecular cyst as a cause of obstructive sleep apnea in an infant
Abstract
A 3-month-old baby was diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) on polysomnography (PSG) with a high apnea hypopnea index (AHI). On further investigations he was found to have a vallecular cyst that was successfully treated. We discuss the clinical presentation of vallecular cysts and the importance of polysomnography in identifying this rare condition.
Keywords: Vallecular cysts; cleft lip and sleep apnea; laryngeal cysts; obstructive sleep apnea in infants.
Figures
References
-
- DeSanto LW, Devine KD, Weiland LH. Cyst of the larynx: classification. Laryngoscope. 1970;80:145–76. - PubMed
-
- Altmeyer VL, Fechner RE. Multiple epiglottic cysts. Arch Otolaryngol. 1978;104:673–5. - PubMed
-
- Gutie'rrez JP, Berkowitz RG, Robertson CF. Vallecular cysts in newborns and young infants. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1999;27:282–5. - PubMed
-
- Sands NB, Anand SM, Manoukian JJ. Series of congenital vallecular cysts: a rare yet potentially fatal cause of upper airway obstruction and failure to thrive in the newborn. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;38:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Prowse S, Knight L. Congenital cysts of the infant larynx. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;76:708–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources