Phenothiazine Inhibitors of TLKs Affect Double-Strand Break Repair and DNA Damage Response Recovery and Potentiate Tumor Killing with Radiomimetic Therapy
- PMID: 23946870
- PMCID: PMC3743153
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601913479020
Phenothiazine Inhibitors of TLKs Affect Double-Strand Break Repair and DNA Damage Response Recovery and Potentiate Tumor Killing with Radiomimetic Therapy
Abstract
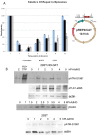
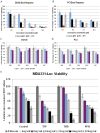
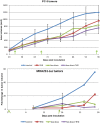
The Tousled-like kinases (TLKs) are involved in chromatin assembly, DNA repair, and transcription. Two TLK genes exist in humans, and their expression is often dysregulated in cancer. TLKs phosphorylate Asf1 and Rad9, regulating double-strand break (DSB) repair and the DNA damage response (DDR). TLKs maintain genomic stability and are important therapeutic intervention targets. We identified specific inhibitors of TLKs from several compound libraries, some of which belong to the family of phenothiazine antipsychotics. The inhibitors prevented the TLK-mediated phosphorylation of Rad9(S328) and impaired checkpoint recovery and DSB repair. The inhibitor thioridazine (THD) potentiated tumor killing with chemotherapy and also had activity alone. Staining for γ-H2AX revealed few positive cells in untreated tumors, but large numbers in mice treated with low doxorubicin or THD alone, possibly the result of the accumulation of DSBs that are not promptly repaired as they may occur in the harsh tumor growth environment.
Keywords: DNA damage response; inhibitors of Tousled kinases; mechanism of DSB repair; radiomimetic sensitizers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
TLK1B promotes repair of DSBs via its interaction with Rad9 and Asf1.BMC Mol Biol. 2009 Dec 20;10:110. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-10-110. BMC Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 20021694 Free PMC article.
-
The Tousled-Like Kinases as Guardians of Genome Integrity.ISRN Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 1;2012:627596. doi: 10.5402/2012/627596. ISRN Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23869254 Free PMC article.
-
Tousled homolog, TLK1, binds and phosphorylates Rad9; TLK1 acts as a molecular chaperone in DNA repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Jan 1;8(1):87-102. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.09.005. Epub 2008 Nov 5. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 18940270
-
Untousling the Role of Tousled-like Kinase 1 in DNA Damage Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13369. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713369. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preserving salivary gland physiology against genotoxic damage - the Tousled way.Oral Dis. 2018 Nov;24(8):1390-1398. doi: 10.1111/odi.12836. Epub 2018 May 2. Oral Dis. 2018. PMID: 29383801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High yield bacterial expression, purification and characterisation of bioactive Human Tousled-like Kinase 1B involved in cancer.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 19;8(1):4796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22744-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29555908 Free PMC article.
-
Tousled-like kinase regulates cytokine-mediated communication between cooperating cell types during collective border cell migration.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 Jan 1;27(1):12-9. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-05-0327. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26510500 Free PMC article.
-
ERα-related chromothripsis enhances concordant gene transcription on chromosome 17q11.1-q24.1 in luminal breast cancer.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 May 14;13(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-0729-7. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32408897 Free PMC article.
-
The TLK1/Nek1 axis contributes to mitochondrial integrity and apoptosis prevention via phosphorylation of VDAC1.Cell Cycle. 2020 Feb;19(3):363-375. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1711317. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Cell Cycle. 2020. PMID: 31914854 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Tousled‑like kinase 1 inhibits survival of glioblastoma multiforme cells.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Aug;46(2):685-699. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4619. Epub 2020 May 28. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32468002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lord CJ, Garrett MD, Ashworth A. Targeting the double-strand DNA break repair pathway as a therapeutic strategy. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(15):4463-8 - PubMed
-
- Sunavala-Dossabhoy G, De Benedetti A. Tousled homolog, TLK1, binds and phosphorylates Rad9: tlk1 acts as a molecular chaperone in DNA repair. DNA Repair. 2009;8:87-102 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
