Noncommunicable diseases: current status of major modifiable risk factors in Korea
- PMID: 23946874
- PMCID: PMC3740221
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.2013.46.4.165
Noncommunicable diseases: current status of major modifiable risk factors in Korea
Abstract
A noncommunicable disease (NCD) is a medical condition or disease that is by definition non-infectious and non-transmissible among people. Currently, NCDs are the leading causes of death and disease burden worldwide. The four main types of NCDs, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic lung disease, and diabetes, result in more than 30 million deaths annually. To reduce the burden of NCDs on global health, current public health actions stress the importance of preventing, detecting, and correcting modifiable risk factors; controlling major modifiable risk factors has been shown to effectively reduce NCD mortality. The World Health Organization's World Health Report 2002 identified tobacco use, alcohol consumption, overweight, physical inactivity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol as the most important risk factors for NCDs. Accordingly, the present report set out to review the prevalence and trends of these modifiable risk factors in the Korean population. Over the past few decades, we observed significant risk factor modifications of improved blood pressure control and decreased smoking rate. However, hypertension and cigarette smoking remained the most contributable factors of NCDs in the Korean population. Moreover, other major modifiable risk factors show no improvement or even worsened. The current status and trends in major modifiable risk factors reinforce the importance of prevention, detection, and treatment of risk factors in reducing the burden of NCDs on individuals and society.
Keywords: Korea; Noncommunicable disease; Prevalence; Risk factors; Trend.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the material presented in this paper.
Figures

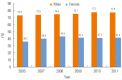

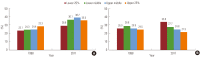

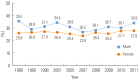
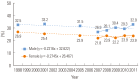


References
-
- Beaglehole R, Bonita R, Horton R, Adams C, Alleyne G, Asaria P, et al. Priority actions for the non-communicable disease crisis. Lancet. 2011;377(9775):1438–1447. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Preventing chronic diseases: a vital investment. [cited 2013 Jul 7]. Available from: http://www.who.int/chp/chronic_disease_report/en.
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory (GHO): deaths from NCDs. [cited 2013 Jul 1]. Available from: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/mortality_morbidity/ncd_total/en/index.html.
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory (GHO): NCD mortality and morbidity. [cited 2013 Jul 17]. Available from: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/mortality_morbidity/en/
-
- World Health Organization. The world health report 2002: reducing risks, promoting healthy life. [cited 2013 Jul 1]. Available from: http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/index.html. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

