Multivitamin supplementation improves haematologic status in children born to HIV-positive women in Tanzania
- PMID: 23948440
- PMCID: PMC3744818
- DOI: 10.7448/IAS.16.1.18022
Multivitamin supplementation improves haematologic status in children born to HIV-positive women in Tanzania
Abstract
Introduction: Anaemia is prevalent among children born to HIV-positive women, and it is associated with adverse effects on cognitive and motor development, growth, and increased risks of morbidity and mortality.
Objective: To examine the effect of daily multivitamin supplementation on haematologic status and mother-to-child transmission (MTCT) of HIV through breastfeeding.
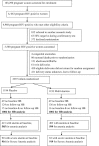
Methods: A total of 2387 infants born to HIV-positive women from Dar es Salaam, Tanzania were enrolled in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, and provided a daily oral supplement of multivitamins (vitamin B complex, C and E) or placebo at age 6 weeks for 24 months. Among them, 2008 infants provided blood samples and had haemoglobin concentrations measured at baseline and during a follow-up period. Anaemia was defined as haemoglobin concentrations <11 g/dL and severe anaemia <8.5 g/dL.
Results: Haemoglobin concentrations among children in the treatment group were significantly higher than those in the placebo group at 12 (9.77 vs. 9.64 g/dL, p=0.03), 18 (9.76 vs. 9.57 g/dL, p=0.004), and 24 months (9.93 vs. 9.75 g/dL, p=0.02) of follow-up. Compared to those in the placebo group, children in the treatment group had a 12% lower risk of anaemia (hazard ratio (HR): 0.88; 95% CI: 0.79-0.99; p=0.03). The treatment was associated with a 28% reduced risk of severe anaemia among children born to women without anaemia (HR: 0.72; 95% CI: 0.56-0.92; p=0.008), but not among those born to women with anaemia (HR: 1.10; 95% CI: 0.79-1.54; p=0.57; p for interaction=0.007). One thousand seven hundred fifty three infants who tested HIV-negative at baseline and had HIV testing during follow-up were included in the analysis for MTCT of HIV. No association was found between multivitamin supplements and MTCT of HIV.
Conclusions: Multivitamin supplements improve haematologic status among children born to HIV-positive women. Further trials focusing on anaemia among HIV-exposed children are warranted in the context of antiretroviral therapy.
Keywords: Tanzania; anaemia; haemoglobin; mother-to-child transmission; multivitamins; randomized controlled trial.
Figures
References
-
- Totin D, Ndugwa C, Mmiro F, Perry RT, Jackson JB, Semba RD. Iron deficiency anaemia is highly prevalent among human immunodeficiency virus-infected and uninfected infants in Uganda. J Nutr. 2002;132(3):423–9. - PubMed
-
- Feiterna-Sperling C, Weizsaecker K, Buhrer C, Casteleyn S, Loui A, Schmitz T, et al. Hematologic effects of maternal antiretroviral therapy and transmission prophylaxis in HIV-1-exposed uninfected newborn infants. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;45(1):43–51. - PubMed
-
- Clark TD, Mmiro F, Ndugwa C, Perry RT, Jackson JB, Melikian G, et al. Risk factors and cumulative incidence of anaemia among human immunodeficiency virus-infected children in Uganda. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2002;22(1):11–7. - PubMed
-
- Fawzi WW, Msamanga GI, Kupka R, Spiegelman D, Villamor E, Mugusi F, et al. Multivitamin supplementation improves hematologic status in HIV-infected women and their children in Tanzania. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;85(5):1335–43. - PubMed
-
- Smuts CM, Lombard CJ, Benade AJ, Dhansay MA, Berger J, Hop le T, et al. Efficacy of a foodlet-based multiple micronutrient supplement for preventing growth faltering, anemia, and micronutrient deficiency of infants: the four country IRIS trial pooled data analysis. J Nutr. 2005;135(3):631S–8S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical