Rho-kinase: regulation, (dys)function, and inhibition
- PMID: 23950574
- PMCID: PMC5538733
- DOI: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0181
Rho-kinase: regulation, (dys)function, and inhibition
Abstract
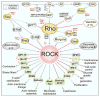
In a variety of normal and pathological cell types, Rho-kinases I and II (ROCKI/II) play a pivotal role in the organization of the nonmuscle and smooth muscle cytoskeleton and adhesion plaques as well as in the regulation of transcription factors. Thus, ROCKI/II activity regulates cellular contraction, motility, morphology, polarity, cell division, and gene expression. Emerging evidence suggests that dysregulation of the Rho-ROCK pathways at different stages is linked to cardiovascular, metabolic, and neurodegenerative diseases as well as cancer. This review focuses on the current status of understanding the multiple functions of Rho-ROCK signaling pathways and various modes of regulation of Rho-ROCK activity, thereby orchestrating a concerted functional response.
Figures
References
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Nakamura N, Kaneko T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. The COOH-terminus of Rho-kinase negatively regulates rho-kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:32418–32424. - PubMed
-
- Antoniu SA. Targeting RhoA/ROCK pathway in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2012;16:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Appels NM, Bolijn MJ, van Eijndhoven MA, Stephens TC, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH. Characterization of the in vitro activity of AZD3409, a novel prenyl transferase inhibitor. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67:137–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
