Reevaluating the role of the hippocampus in delay eyeblink conditioning
- PMID: 23951119
- PMCID: PMC3739805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071249
Reevaluating the role of the hippocampus in delay eyeblink conditioning
Abstract
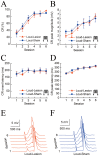
The role of the hippocampus in delay eyeblink conditioning (DEC) remains controversial. Here, we investigated the involvement of the hippocampus in DEC with a soft tone as the conditioned stimulus (CS) by using electrolytic lesions or muscimol inactivation of guinea pig dorsal hippocampus. Interestingly, when a soft tone was used as a CS, electrolytic lesions of the hippocampus significantly retarded acquisition of the conditioned response (CR), and muscimol infusions into hippocampus distinctly inhibited the acquisition and expression of CR, but had no significant effect on consolidation of well-learned CR. In contrast, both electrolytic lesions and muscimol inactivation of hippocampus produced no significant deficits in the CR when a loud tone was used as the CS. These results demonstrate that the hippocampus is essential for the DEC when the delay task was rendered more difficult.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Reevaluating the role of the medial prefrontal cortex in delay eyeblink conditioning.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012 Mar;97(3):277-88. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Feb 26. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2012. PMID: 22387661
-
Disrupted topography of the acquired trace-conditioned eyeblink responses in guinea pigs after suppression of cerebellar cortical inhibition to the interpositus nucleus.Brain Res. 2010 Jun 14;1337:41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.03.089. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20381463
-
Inactivation of the interpositus nucleus blocks the acquisition of conditioned responses and timing changes in conditioning-specific reflex modification of the rabbit eyeblink response.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Nov;155:143-156. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 30053576 Free PMC article.
-
Brain mechanisms of extinction of the classically conditioned eyeblink response.Learn Mem. 2004 Sep-Oct;11(5):517-24. doi: 10.1101/lm.80004. Learn Mem. 2004. PMID: 15466302 Review.
-
Eyeblink conditioning and systems consolidation: an ironic yet powerful pairing.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011 Feb;95(2):118-24. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.12.003. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2011. PMID: 21145979 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic stimulation of mPFC pyramidal neurons as a conditioned stimulus supports associative learning in rats.Sci Rep. 2015 May 14;5:10065. doi: 10.1038/srep10065. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25973929 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic inhibition of ventral hippocampal neurons alleviates associative motor learning dysfunction in a rodent model of schizophrenia.PLoS One. 2019 Dec 31;14(12):e0227200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227200. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31891640 Free PMC article.
-
The hearing hippocampus.Prog Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;218:102326. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2022.102326. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35870677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timing and expectation of reward: a neuro-computational model of the afferents to the ventral tegmental area.Front Neurorobot. 2014 Jan 31;8:4. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2014.00004. eCollection 2014. Front Neurorobot. 2014. PMID: 24550821 Free PMC article.
-
Reevaluating the ability of cerebellum in associative motor learning.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 15;9(1):6029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42413-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30988338 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christian KM, Thompson RF (2003) Neural substrates of eyeblink conditioning: acquisition and retention. Learn Mem 10: 427–455. - PubMed
-
- Christian KM, Thompson RF (2005) Long-term storage of an associative memory trace in the cerebellum. Behav Neurosci 119: 526–537. - PubMed
-
- Thompson RF (2005) In search of memory traces. Annu Rev Psychol 56: 1–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

