Inhibitory peptide of mitochondrial μ-calpain protects against photoreceptor degeneration in rhodopsin transgenic S334ter and P23H rats
- PMID: 23951212
- PMCID: PMC3739725
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071650
Inhibitory peptide of mitochondrial μ-calpain protects against photoreceptor degeneration in rhodopsin transgenic S334ter and P23H rats
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(9). doi:10.1371/annotation/7a8aaf1d-e968-4b39-abb0-867d6078b2af
Abstract
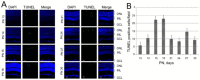
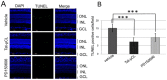
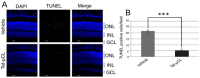
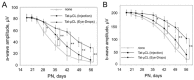
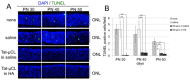
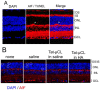
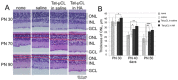
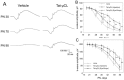
Mitochondrial μ-calpain and apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF)-dependent photoreceptor cell death has been seen in several rat and mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa (RP). Previously, we demonstrated that the specific peptide inhibitor of mitochondrial μ-calpain, Tat-µCL, protected against retinal degeneration following intravitreal injection or topical eye-drop application in Mertk gene-mutated Royal College of Surgeons rats, one of the animal models of RP. Because of the high rate of rhodopsin mutations in RP patients, the present study was performed to confirm the protective effects of Tat-µCL against retinal degeneration in rhodopsin transgenic S334ter and P23H rats. We examined the effects of intravitreal injection or topical application of the peptide on retinal degeneration in S334ter and P23H rats by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay, electroretinogram (ERG), immunohistochemistry for AIF, and histological staining. In S334ter rats, we found that intravitreal injection or topical application of the peptide prevented photoreceptor cell death from postnatal (PN) 15 to 18 days, the time of early-stage retinal degeneration. Topical application of the peptide also delayed attenuation of ERG responses from PN 28 to 56 days. In P23H rats, topical application of the peptide protected against photoreceptor cell death and nuclear translocation of AIF on PN 30, 40, and 50 days, as the primary stages of degeneration. We observed that topical application of the peptide inhibited the thinning of the outer nuclear layer and delayed ERG attenuations from PN 30 to 90 days. Our results demonstrate that the mitochondrial μ-calpain and AIF pathway is involved in early-stage retinal degeneration in rhodopsin transgenic S334ter and P23H rats, and inhibition of this pathway shows curative potential for rhodopsin mutation-caused RP.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravitreal injection or topical eye-drop application of a μ-calpain C2L domain peptide protects against photoreceptor cell death in Royal College of Surgeons' rats, a model of retinitis pigmentosa.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Nov;1822(11):1783-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.07.018. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22885154
-
Decrease of ATP by mitochondrial m-calpain inhibitory peptide in the rat retinas.Cell Struct Funct. 2013;38(2):207-23. doi: 10.1247/csf.13008. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Cell Struct Funct. 2013. PMID: 23965546
-
The heat-shock response co-inducer arimoclomol protects against retinal degeneration in rhodopsin retinitis pigmentosa.Cell Death Dis. 2014 May 22;5(5):e1236. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.214. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 24853414 Free PMC article.
-
[New drug therapy for retinal degeneration].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008 Jan;112(1):7-21. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18240599 Review. Japanese.
-
Optical Coherence Tomography of Animal Models of Retinitis Pigmentosa: From Animal Studies to Clinical Applications.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Oct 30;2019:8276140. doi: 10.1155/2019/8276140. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31781647 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cationic Arginine-Rich Peptides (CARPs): A Novel Class of Neuroprotective Agents With a Multimodal Mechanism of Action.Front Neurol. 2020 Feb 25;11:108. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00108. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32158425 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of Topically Applied Calpain Inhibitory Peptide to the Posterior Segment of the Rat Eye.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 24;10(6):e0130986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130986. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26107400 Free PMC article.
-
A role of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Photoreceptor Cell Death: Potential as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Retinal Degeneration.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016 Jan;22(1):7-14. doi: 10.1111/cns.12471. Epub 2015 Oct 28. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2016. PMID: 26507240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cGMP-signalling and calcium-signalling in photoreceptor cell death: perspectives for therapy development.Pflugers Arch. 2021 Sep;473(9):1411-1421. doi: 10.1007/s00424-021-02556-9. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Pflugers Arch. 2021. PMID: 33864120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAPN5 genetic inactivation phenotype supports therapeutic inhibition trials.Hum Mutat. 2019 Dec;40(12):2377-2392. doi: 10.1002/humu.23894. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Hum Mutat. 2019. PMID: 31403230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang GQ, Hao Y, Wong F (1993) Apoptosis: final common pathway of photoreceptor death in rd, rds, and rhodopsin mutant mice. Neuron 11: 595–605. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

