Presenilin 2 influences miR146 level and activity in microglia
- PMID: 23952003
- PMCID: PMC4346352
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12400
Presenilin 2 influences miR146 level and activity in microglia
Abstract
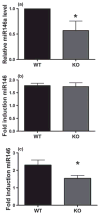
Microglia, the resident innate immune cells of the CNS, are the primary defenders against microbes and critical to CNS remodeling. Dysregulation of microglial behavior can lead to unchecked pro-inflammatory activity and subsequent neurodegeneration. The molecular mechanisms leading to chronic inflammation and microglial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases are not well-understood. It is known that patients with Presenilin 2 (PS2) mutations develop autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease. We have shown that a lack of normal PS2 function is associated with exaggerated microglia pro-inflammatory responses in vitro. To identify pathways by which PS2 regulates microglia and determine how PS2 dysfunction may lead to altered inflammatory pathways, we pursued an unbiased array approach to assess differential expression of microRNAs between murine PS2 knockout (KO) and wild-type microglia. We identified miR146, a negative regulator of monocyte pro-inflammatory response, as constitutively down-regulated in PS2 KO microglia. Consistent with a state of miR146 suppression, we found that PS2 KO microglia express higher levels of the miR146 target protein interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1, and have increased NFκB transcriptional activity. We hypothesize that PS2 impacts microglial responses through modulation of miR146a. PS2 dysfunction, through aging or mutation, may contribute to neurodegeneration by influencing the pro-inflammatory behavior of microglia. Presenilin 2 (PS2), a membrane associated protease, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. We have previously shown that PS2 plays an important role in curbing the proinflammatory response in microglia. Here, we report the novel finding that PS2 participates in maintaining the basal and cytokine induced expression of the innate immunity regulating microRNA, miR146. These data suggest one mechanism by which PS2 works to reign in proinflammatory microglial behavior and that PS2 dysfunction or deficiency could thus result in unchecked proinflammatory activation contributing to neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; miR146; microglia; neuroinflammation; presenilin.
© 2013 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Presenilin 2 is the predominant γ-secretase in microglia and modulates cytokine release.PLoS One. 2010 Dec 29;5(12):e15743. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015743. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21206757 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin 2 deficiency facilitates Aβ-induced neuroinflammation and injury by upregulating P2X7 expression.Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Feb;60(2):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-0347-4. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28120269
-
Early-Onset Familial Alzheimer Disease Variant PSEN2 N141I Heterozygosity is Associated with Altered Microglia Phenotype.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;77(2):675-688. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200492. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32741831 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal injury in chronic CNS inflammation.Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2010 Dec;24(4):551-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bpa.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol. 2010. PMID: 21619866 Review.
-
The p53 Transcriptional Network Influences Microglia Behavior and Neuroinflammation.Crit Rev Immunol. 2015;35(5):401-15. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v35.i5.40. Crit Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26853851 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs as Potential Orchestrators of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Pathologies: Insights on Current Status and Future Possibilities.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Oct 12;13:743573. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.743573. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34712129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The involvement of microRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Dec 19;7:265. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00265. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24391543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-124 regulates the expression of MEKK3 in the inflammatory pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jan 12;15(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1053-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29329581 Free PMC article.
-
Causes and Consequences of MicroRNA Dysregulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):1249-62. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8803-9. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24973986 Review.
-
The pro-inflammatory microRNA miR-155 influences fibrillar β-Amyloid1-42 catabolism by microglia.Glia. 2021 Jul;69(7):1736-1748. doi: 10.1002/glia.23988. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Glia. 2021. PMID: 33694209 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Beglopoulos V, Sun X, Saura CA, Lemere CA, Kim RD, Shen J. Reduced beta-amyloid production and increased inflammatory responses in presenilin conditional knock-out mice. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:46907–46914. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Henzel WJ, Gao X. IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science. 1996;271:1128–1131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

