A C-C bonded phenoxyl radical dimer with a zero bond dissociation free energy
- PMID: 23952108
- PMCID: PMC4084963
- DOI: 10.1021/ja406500h
A C-C bonded phenoxyl radical dimer with a zero bond dissociation free energy
Abstract
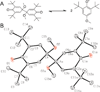
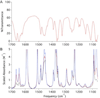
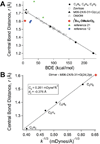
The 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methoxyphenoxyl radical is shown to dimerize in solution and in the solid state. The X-ray crystal structure of the dimer, the first for a para-coupled phenoxyl radical, revealed a bond length of 1.6055(23) Å for the C4-C4a bond. This is significantly longer than typical C-C bonds. Solution equilibrium studies using both optical and IR spectroscopies showed that the Keq for dissociation is 1.3 ± 0.2 M at 20 °C, indicating a C-C bond dissociation free energy of -0.15 ± 0.1 kcal mol(-1). Van't Hoff analysis gave an exceptionally small bond dissociation enthalpy (BDE) of 6.1 ± 0.5 kcal mol(-1). To our knowledge, this is the smallest BDE measured for a C-C bond. This very weak bond shows a large deviation from the correlation of C-C bond lengths and strengths, but the computed force constant follows Badger's rule.
Figures
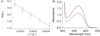
References
-
- Zavitsas AA. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2003;107:897–898.
- Dames E, Sirjean B, Wang H. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2010;114:1161–1168. - PubMed
-
-
Badger RM. J. Chem. Phys. 1934;2:128–131. Badger RM. J. Chem. Phys. 1935;3:710–714. For a recent application, see Green MT. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:1902–1906.
-
-
- Pauling L. The Nature of the Chemical Bond and the Structure of Molecules and Crystals . 3d ed. Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press; 1960.
-
- Brown ID, Shannon RD. Acta Cryst. A. 1973;A 29:266–282.
-
- Collman JP, Decreau RA, Sunderland CJ. Chem. Commun. 2006:3894–3896. - PubMed
- Schrauben JN, Hayoun R, Valdez CN, Braten M, Fridley L, Mayer JM. Science. 2012;336:1298–1301. - PubMed
- Lyons CT, Stack TDP. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013;257:528–540. - PMC - PubMed
- Lucarini M, Pedulli GF. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010;39:2106–2119. - PubMed
- Markle TF, Tronic TA, DiPasquale AG, Kaminsky W, Mayer JM. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2012;116:12249–12259. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

