Reproducibility of speckle-tracking-based strain measures of left ventricular function in a community-based study
- PMID: 23953701
- PMCID: PMC3812381
- DOI: 10.1016/j.echo.2013.07.002
Reproducibility of speckle-tracking-based strain measures of left ventricular function in a community-based study
Abstract
Background: The reproducibility of echocardiographic measurements of myocardial strain, performed in a community-based setting, has not been reported previously.
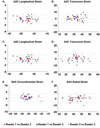
Methods: The reproducibility of left ventricular strain measurements was examined in two samples of 20 participants each from the Offspring Cohort of the Framingham Heart Study (mean age, 63 ± 9 years; 59% women). Two-dimensional speckle-tracking-based measurements of global peak left ventricular strain in systole were performed in the apical four-chamber, apical two-chamber, and midventricular parasternal short-axis views.
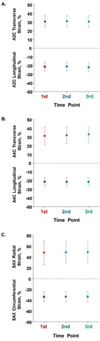
Results: Interobserver intraclass correlation coefficients were ≥0.84 for all global strain measurements, with average coefficients of variation of ≤4% for global longitudinal and circumferential strain and <8% for global transverse and radial strain. For left ventricular strain measurements performed in each of the three views, intraobserver intraclass correlation coefficients were ≥0.91 among time points spanning a total 8-month period. The average coefficients of variation were <6% for global longitudinal and circumferential strain and <9% for global transverse and radial strain. Interobserver and intraobserver reproducibility findings were similar in analyses adjusting for frame rate.
Conclusions: Excellent reproducibility of global longitudinal and circumferential strain measurements and very good reproducibility of global transverse and radial strain measurements were observed. Taken together, these findings demonstrate the reproducibility of performing echocardiographic strain measurements in a large, epidemiologic community-based setting.
Keywords: A2C; A4C; Apical four-chamber; Apical two-chamber; Epidemiology; ICC; Intraclass correlation coefficient; LV; Left ventricular; Myocardial deformation; SAX; Short-axis; Speckle-tracking; Strain.
Copyright © 2013 American Society of Echocardiography. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
-
- Shah AM, Solomon SD. Myocardial deformation imaging: current status and future directions. Circulation. 2012;125:e244–e248. - PubMed
-
- Amundsen BH, Helle-Valle T, Edvardsen T, Torp H, Crosby J, Lyseggen E, et al. Noninvasive myocardial strain measurement by speckle tracking echocardiography: validation against sonomicrometry and tagged magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:789–793. - PubMed
-
- Langeland S, D’Hooge J, Wouters PF, Leather HA, Claus P, Bijnens B, et al. Experimental validation of a new ultrasound method for the simultaneous assessment of radial and longitudinal myocardial deformation independent of insonation angle. Circulation. 2005;112:2157–2162. - PubMed
-
- Korinek J, Wang J, Sengupta PP, Miyazaki C, Kjaergaard J, McMahon E, et al. Two-dimensional strain--a Doppler-independent ultrasound method for quantitation of regional deformation: validation in vitro and in vivo. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005;18:1247–1253. - PubMed
-
- Stanton T, Leano R, Marwick TH. Prediction of all-cause mortality from global longitudinal speckle strain: comparison with ejection fraction and wall motion scoring. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009;2:356–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

