Extracellular potassium homeostasis: insights from hypokalemic periodic paralysis
- PMID: 23953801
- PMCID: PMC4131448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2013.04.004
Extracellular potassium homeostasis: insights from hypokalemic periodic paralysis
Abstract
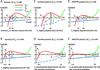
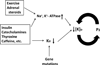
Extracellular potassium makes up only about 2% of the total body's potassium store. The majority of the body potassium is distributed in the intracellular space, of which about 80% is in skeletal muscle. Movement of potassium in and out of skeletal muscle thus plays a pivotal role in extracellular potassium homeostasis. The exchange of potassium between the extracellular space and skeletal muscle is mediated by specific membrane transporters. These include potassium uptake by Na(+), K(+)-adenosine triphosphatase and release by inward-rectifier K(+) channels. These processes are regulated by circulating hormones, peptides, ions, and by physical activity of muscle as well as dietary potassium intake. Pharmaceutical agents, poisons, and disease conditions also affect the exchange and alter extracellular potassium concentration. Here, we review extracellular potassium homeostasis, focusing on factors and conditions that influence the balance of potassium movement in skeletal muscle. Recent findings that mutations of a skeletal muscle-specific inward-rectifier K(+) channel cause hypokalemic periodic paralysis provide interesting insights into the role of skeletal muscle in extracellular potassium homeostasis. These recent findings are reviewed.
Keywords: Hypokalemic periodic paralysis; K(+)-ATPase; Kir; Na(+); hypokalemia-induced paradoxical depolarization; inward-rectifier K(+) channel; skeletal muscle; thyrotoxic periodic paralysis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Sejersted OM, Sjøgaard G. Dynamics and consequences of potassium shifts in skeletal muscle and heart during exercise. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:1411–1481. - PubMed
-
- Sjøgaard G, Adams RP, Saltin B. Water and ion shifts in skeletal muscle of humans with intense dynamic knee extension. Am J Physiol. 1985;248:R190–R196. - PubMed
-
- Skou JC. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957;23:394–401. - PubMed
-
- Skou JC. Enzymatic basis for active transport of Na+ and K+ across cell membrane. Physiol Rev. 1965;45:596–617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

