The use of self-adjuvanting nanofiber vaccines to elicit high-affinity B cell responses to peptide antigens without inflammation
- PMID: 23953841
- PMCID: PMC3814015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.063
The use of self-adjuvanting nanofiber vaccines to elicit high-affinity B cell responses to peptide antigens without inflammation
Abstract
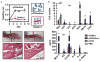
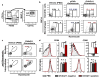
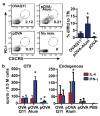
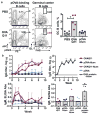
Balancing immunogenicity with inflammation is a central tenet of vaccine design, especially for subunit vaccines that utilize traditional pro-inflammatory adjuvants. Here we report that by using a nanoparticulate peptide-based vaccine, immunogenicity and local inflammation could be decoupled. Self-assembled β-sheet-rich peptide nanofibers, previously shown to elicit potent antibody responses in mice, were found to be non-cytotoxic in vitro and, remarkably, elicited no measurable inflammation in vivo-with none of the swelling at the injection site, accumulation of inflammatory cells or cytokines, or production of allergic IgE that were elicited by an alum-adjuvanted vaccine. Nanofibers were internalized by dendritic cells and macrophages at the injection site, and only dendritic cells that acquired the material increased their expression of the activation markers CD80 and CD86. Immunization with epitope-bearing nanofibers elicited antigen-specific differentiation of T cells into T follicular helper cells and B cells into germinal center cells, as well as high-titer, high-affinity IgG that cross-reacted with the native protein antigen and was neutralizing in an in vitro influenza hemagglutination inhibition assay. These responses were superior to those induced by alum and comparable to those induced by complete Freund's adjuvant. Thus, nanoparticulate assemblies may provide a new route to non-inflammatory immunotherapies and vaccines.
Keywords: Alum adjuvant; Nanoparticle vaccines; Non-reactogenic; OVA(323-339) peptide; Self assembly.
© 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures

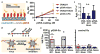
References
-
- Aguilar JC, Rodriguez EG. Vaccine adjuvants revisited. Vaccine. 2007;25:3752–62. - PubMed
-
- Reed SG, Bertholet S, Coler RN, Friede M. New horizons in adjuvants for vaccine development. Trends Immunol. 2009;30:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Dekker CL, Gordon L, Klein J. Dose optimization strategies for vaccines: the role of adjuvants and new technologies. Vaccine Development and Supply Subcommittee of the National Vaccine Advisory Committee; 2008.
-
- Gupta RK. Aluminum compounds as vaccine adjuvants. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1998;32:155–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

