Acute antibody-mediated rejection after lung transplantation
- PMID: 23953920
- PMCID: PMC3822761
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2013.07.004
Acute antibody-mediated rejection after lung transplantation
Abstract
Background: Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) after lung transplantation remains enigmatic, and there is no consensus on the characteristic clinical, immunologic and histologic features.
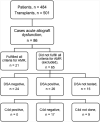
Methods: We performed a retrospective, single-center cohort study and identified cases of acute AMR based on the presence of circulating donor-specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) antibodies (DSA), histologic evidence of acute lung injury, C4d deposition and clinical allograft dysfunction.
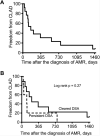
Results: We identified 21 recipients with acute AMR based on the aforementioned criteria. AMR occurred a median 258 days after transplantation; 7 recipients developed AMR within 45 days of transplantation. All patients had clinical allograft dysfunction, DSA, histology of acute lung injury and capillary endothelial C4d deposition. Fifteen recipients improved clinically and survived to hospital discharge, but 6 died of refractory AMR. One survivor had bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome at the time of AMR diagnosis; 13 of the 14 remaining survivors developed chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD) during follow-up. Overall, 15 recipients died during the study period, and the median survival after the diagnosis of AMR was 593 days.
Conclusions: Acute AMR can be a fulminant form of lung rejection, and survivors are at increased risk of developing CLAD. The constellation of acute lung injury, DSA and capillary endothelial C4d deposition is compelling for acute AMR in recipients with allograft dysfunction. This clinicopathologic definition requires validation in a multicenter cohort, but may serve as a foundation for future studies to further characterize AMR.
Keywords: C4d deposition; acute antibody-mediated rejection; chronic lung allograft dysfunction; donor specific antibodies; human leukocyte antigen antibodies; lung transplantation.
© 2013 International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Thabut G, Christie JD, Kremers WK, Fournier M, Halpern SD. Survival differences following lung transplantation among US transplant centers. JAMA. 2010;304:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: 29th adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2012. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012;31:1073–86. - PubMed
-
- Bhorade SM, Stern E. Immunosuppression for lung transplantation. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2009;6:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Durrbach A, Francois H, Beaudreuil S, Jacquet A, Charpentier B. Advances in immunosuppression for renal transplantation. Nature reviews Nephrology. 2010;6:160–7. - PubMed
-
- Jeannet M, Pinn VW, Flax MH, Winn HJ, Russell PS. Humoral antibodies in renal allotransplantation in man. N Engl J Med. 1970;282:111–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

