Successes and challenges of using whole exome sequencing to identify novel genes underlying an inherited predisposition for thoracic aortic aneurysms and acute aortic dissections
- PMID: 23953976
- PMCID: PMC3917689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2013.06.004
Successes and challenges of using whole exome sequencing to identify novel genes underlying an inherited predisposition for thoracic aortic aneurysms and acute aortic dissections
Abstract
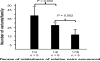
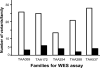
Thoracic aortic aneurysms involving the aortic root and/or ascending aorta can lead to acute aortic dissections. Approximately 20% of patients with thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections (TAAD) have a family history of the disease, referred to as familial TAAD (FTAAD) that can be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner with variable expression with respect to disease presentation, age of onset and associated features. Whole exome sequencing (WES) has been used to identify causative mutations in novel genes for TAAD. The strategy used to reduce the large number of rare variants identified using WES is to sequence distant relatives with TAAD and filter for heterozygous rare variants that are shared between the relatives, predicted to disrupt protein function and segregate with the TAAD phenotype in other family members. Putative genes are validated by identifying additional families with a causative mutation in the genes. This approach has successfully identified novel genes for FTAAD.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

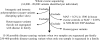
References
-
- Albornoz G, Coady MA, Roberts M, et al. Familial thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections--incidence, modes of inheritance, and phenotypic patterns. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82:1400–1405. - PubMed
-
- Biddinger A, Rocklin M, Coselli J, et al. Familial thoracic aortic dilatations and dissections: a case control study. J Vasc Surg. 1997;25:506–511. - PubMed
-
- Coady MA, Davies RR, Roberts M, et al. Familial patterns of thoracic aortic aneurysms. Arch Surg. 1999;134:361–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL062594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL62594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL110869/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102926/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-103010/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50HL083794-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102924/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UC2 HL102925/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL083794/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000371/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL109942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

