Viruses PLAY DEAD to TAMe interferon responses
- PMID: 23954149
- PMCID: PMC3780386
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.014
Viruses PLAY DEAD to TAMe interferon responses
Abstract
TAM receptors promote apoptotic cell uptake and function as inflammation suppressors. Many viruses mimic apoptotic cells, thus exploiting TAM receptors for attachment and entry. In this issue of Cell Host & Microbe, Bhattacharyya et al. show that TAM binding by enveloped viruses also induces receptor signaling to suppress cellular interferon responses.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
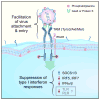
Comment on
-
Enveloped viruses disable innate immune responses in dendritic cells by direct activation of TAM receptors.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Aug 14;14(2):136-47. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.005. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23954153 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

