Kinesin-5: cross-bridging mechanism to targeted clinical therapy
- PMID: 23954229
- PMCID: PMC3801170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.08.004
Kinesin-5: cross-bridging mechanism to targeted clinical therapy
Abstract
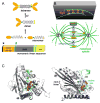
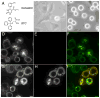
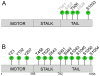
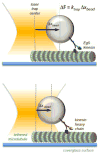
Kinesin motor proteins comprise an ATPase superfamily that works hand in hand with microtubules in every eukaryote. The mitotic kinesins, by virtue of their potential therapeutic role in cancerous cells, have been a major focus of research for the past 28 years since the discovery of the canonical Kinesin-1 heavy chain. Perhaps the simplest player in mitotic spindle assembly, Kinesin-5 (also known as Kif11, Eg5, or kinesin spindle protein, KSP) is a plus-end-directed motor localized to interpolar spindle microtubules and to the spindle poles. Comprised of a homotetramer complex, its function primarily is to slide anti-parallel microtubules apart from one another. Based on multi-faceted analyses of this motor from numerous laboratories over the years, we have learned a great deal about the function of this motor at the atomic level for catalysis and as an integrated element of the cytoskeleton. These data have, in turn, informed the function of motile kinesins on the whole, as well as spearheaded integrative models of the mitotic apparatus in particular and regulation of the microtubule cytoskeleton in general. We review what is known about how this nanomotor works, its place inside the cytoskeleton of cells, and its small-molecule inhibitors that provide a toolbox for understanding motor function and for anticancer treatment in the clinic.
Keywords: ADP; AMPPNP; AP1; ATP; ATP hydrolysis; Allosteric inhibition; CDK1; DMSO; DNA; Eg5; GFP; GTP; ICL; KHC; KSP; Kinesin; L5; MT; Mitosis; NCBI; NER; NTP; NTPases; National Center for Biotechnology Information; P loop; P(i); PDB; Protein DataBank; RNAi; RefSeq; Reference Sequence; S-trityl-l-cysteine; STC; Traf4; XPF; Xeroderma pigmentosum group F; activator protein 1; adenosine diphosphate; adenosine-5′-(β,γ-imido)triphosphate; adenosine-5′-triphosphate; cryo-EM; cryo-electron microscopy; cyclin-dependent kinase 1; deoxyribonucleic acid; dimethyl sulfoxide; double stranded ribonucleic acid interference; dsRNAi; green fluorescent protein; guanosine-5′-triphosphate; inorganic phosphate; interstrand DNA cross-linking; kDa; kilodalton; kinesin heavy chain; kinesin spindle protein; loop 5; microtubule; nucleotide excision repair; nucleotide triphosphatases; nucleotide triphosphate; pN; phosphate-binding loop; piconewton; ribonucleic acid interference; siRNA; small interfering ribonucleic acid; tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 4.
© 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Asenjo AB, Krohn N, Sosa H. Configuration of the two kinesin motor domains during ATP hydrolysis. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:836–42. - PubMed
-
- Bannigan A, Scheible WR, Lukowitz W, Fagerstrom C, Wadsworth P, Somerville C, Baskin TI. A conserved role for kinesin-5 in plant mitosis. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:2819–27. - PubMed
-
- Beer T, Goldman B, Synold T, Ryan C, Vasist L, Van Veldhuizen P, Dakhil S, Lara P, Drelichman A, Hussain M, Crawford E. Southwest Oncology Group phase II study of ispinesib in androgen-independent prostate cancer previously treated with taxanes. Clinical Genitourinary Cancer. 2008;6:103–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

