SIV antigen-specific effects on immune responses induced by vaccination with DNA electroporation and plasmid IL-12
- PMID: 23954384
- PMCID: PMC7570371
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.011
SIV antigen-specific effects on immune responses induced by vaccination with DNA electroporation and plasmid IL-12
Abstract
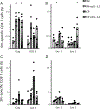
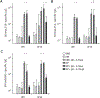
Molecular adjuvants are important for augmenting or modulating immune responses induced by DNA vaccination. Promising results have been obtained using IL-12 expression plasmids in a variety of disease models including the SIV model of HIV infection. We used a mouse model to evaluate plasmid IL-12 (pIL-12) in a DNA prime, recombinant adenovirus serotype 5 (rAd5) boost regimen specifically to evaluate the effect of IL-12 expression on cellular and humoral immunity induced against both SIVmac239 Gag and Env antigens. Priming with electroporated (EP) DNA+pIL-12 resulted in a 2-4-fold enhanced frequency of Gag-specific CD4 T cells which was maintained through the end of the study irrespective of the pIL-12 dose, while memory Env-specific CD4+T cells were maintained only at the low dose of pIL-12. There was little positive effect of pIL-12 on the humoral response to Env, and in fact, high dose pIL-12 dramatically reduced SIV Env-specific IgG. Additionally, both doses of pIL-12 diminished the frequency of CD8 T-cells after DNA prime, although a rAd5 boost recovered CD8 responses regardless of the pIL-12 dose. In this prime-boost regimen, we have shown that a high dose pIL-12 can systemically reduce Env-specific humoral responses and CD4T cell frequency, but not Gag-specific CD4+ T cells. These data indicate that it is important to independently characterize individual SIV or HIV antigen immunogenicity in multi-antigenic vaccines as a function of adjuvant dose.
Keywords: Adenovirus; Antibody; DNA; IL-12; T cell.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
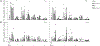



Similar articles
-
Enhanced control of pathogenic Simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 replication in macaques immunized with an interleukin-12 plasmid and a DNA prime-viral vector boost vaccine regimen.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(18):9578-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05060-11. Epub 2011 Jul 6. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21734035 Free PMC article.
-
CD40L-adjuvanted DNA/modified vaccinia virus Ankara simian immunodeficiency virus SIV239 vaccine enhances SIV-specific humoral and cellular immunity and improves protection against a heterologous SIVE660 mucosal challenge.J Virol. 2014 Sep 1;88(17):9579-89. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00975-14. Epub 2014 Jun 11. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24920805 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Priming Increases Frequency of T-Cell Responses to a Vesicular Stomatitis Virus HIV Vaccine with Specific Enhancement of CD8+ T-Cell Responses by Interleukin-12 Plasmid DNA.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017 Nov 6;24(11):e00263-17. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00263-17. Print 2017 Nov. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28931520 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Repeated DNA therapeutic vaccination of chronically SIV-infected macaques provides additional virological benefit.Vaccine. 2010 Feb 23;28(8):1962-74. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.099. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20188252 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of viral loads by multigenic DNA priming and adenovirus boosting in the SIVmac-macaque model.Vaccine. 2006 Mar 10;24(11):1811-20. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.10.026. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16274888
Cited by
-
Mucosal Vaccine Approaches for Prevention of HIV and SIV Transmission.Curr Immunol Rev. 2019;15(1):102-122. doi: 10.2174/1573395514666180605092054. Curr Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31452652 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Heterologous Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIVsmE660 Infection by DNA and Protein Coimmunization Regimens Combined with Different Toll-Like-Receptor-4-Based Adjuvants in Macaques.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00281-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00281-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29793957 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive HIV Vaccines-Leveraging on Lessons from the Past to Pave the Way Forward.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Sep 8;9(9):1001. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9091001. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34579238 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Vaccine-Induced Long-Lasting Cytotoxic T Cells Targeting Conserved Elements of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Gag Are Boosted Upon DNA or Recombinant Modified Vaccinia Ankara Vaccination.Hum Gene Ther. 2018 Sep;29(9):1029-1043. doi: 10.1089/hum.2018.065. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Hum Gene Ther. 2018. PMID: 29869530 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic adjuvants: A paradigm shift in vaccine development and immune modulation.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025 Apr 8;36(2):102536. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102536. eCollection 2025 Jun 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2025. PMID: 40336572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- MacGregor RR, Boyer JD, Ugen KE, Lacy KE, Gluckman SJ, Bagarazzi ML, et al. First human trial of a DNA-based vaccine for treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: safety and host response. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1998;178(July (1)):92–100. - PubMed
-
- Babiuk S, van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S, Babiuk LA. Delivery of DNA vaccines using electroporation. Methods in Molecular Medicine 2006;127:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Barouch DH, Santra S, Schmitz JE, Kuroda MJ, Fu TM, Wagner W, et al. Control of viremia and prevention of clinical AIDS in rhesus monkeys by cytokine-augmented DNA vaccination. Science 2000;290(October (5491)):486–92. - PubMed
-
- Buchan S, Gronevik E, Mathiesen I, King CA, Stevenson FK, Rice J. Electroporation as a prime/boost strategy for naked DNA vaccination against a tumor antigen. Journal of Immunology 2005;174(May (10)):6292–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

