ACE2 alterations in kidney disease
- PMID: 23956234
- PMCID: PMC3811059
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gft320
ACE2 alterations in kidney disease
Abstract
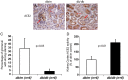
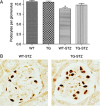
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a monocarboxypeptidase that degrades angiotensin (Ang) II to Ang-(1-7). ACE2 is highly expressed within the kidneys, it is largely localized in tubular epithelial cells and less prominently in glomerular epithelial cells and in the renal vasculature. ACE2 activity has been shown to be altered in diabetic kidney disease, hypertensive renal disease and in different models of kidney injury. There is often a dissociation between tubular and glomerular ACE2 expression, particularly in diabetic kidney disease where ACE2 expression is increased at the tubular level but decreased at the glomerular level. In this review, we will discuss alterations in circulating and renal ACE2 recently described in different renal pathologies and disease models as well as their possible significance.
Keywords: ACE2; kidney disease; renin–angiotensin system.
Figures
References
-
- Crackower MA, Sarao R, Oudit GY, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature. 2002;417:822–828. - PubMed
-
- Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res. 2000;87:E1–E9. - PubMed
-
- Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, et al. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:33238–33243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

