Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society
- PMID: 23956253
- PMCID: PMC3844152
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht273
Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society
Erratum in
-
Editor's Note: Relates to: 'Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease : Consensus Statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society '.Eur Heart J. 2020 Dec 14;41(47):4517. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa166. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32167556 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
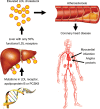
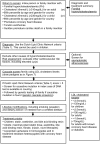
Aims: The first aim was to critically evaluate the extent to which familial hypercholesterolaemia (FH) is underdiagnosed and undertreated. The second aim was to provide guidance for screening and treatment of FH, in order to prevent coronary heart disease (CHD).
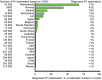
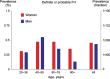
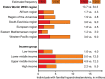
Methods and results: Of the theoretical estimated prevalence of 1/500 for heterozygous FH, <1% are diagnosed in most countries. Recently, direct screening in a Northern European general population diagnosed approximately 1/200 with heterozygous FH. All reported studies document failure to achieve recommended LDL cholesterol targets in a large proportion of individuals with FH, and up to 13-fold increased risk of CHD. Based on prevalences between 1/500 and 1/200, between 14 and 34 million individuals worldwide have FH. We recommend that children, adults, and families should be screened for FH if a person or family member presents with FH, a plasma cholesterol level in an adult ≥8 mmol/L(≥310 mg/dL) or a child ≥6 mmol/L(≥230 mg/dL), premature CHD, tendon xanthomas, or sudden premature cardiac death. In FH, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol targets are <3.5 mmol/L(<135 mg/dL) for children, <2.5 mmol/L(<100 mg/dL) for adults, and <1.8 mmol/L(<70 mg/dL) for adults with known CHD or diabetes. In addition to lifestyle and dietary counselling, treatment priorities are (i) in children, statins, ezetimibe, and bile acid binding resins, and (ii) in adults, maximal potent statin dose, ezetimibe, and bile acid binding resins. Lipoprotein apheresis can be offered in homozygotes and in treatment-resistant heterozygotes with CHD.
Conclusion: Owing to severe underdiagnosis and undertreatment of FH, there is an urgent worldwide need for diagnostic screening together with early and aggressive treatment of this extremely high-risk condition.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Cardiovascular disease; Cholesterol; Coronary heart disease; Low-density lipoprotein.
Figures

References
-
- Goldstein JK, Hobbs HH, Brown MS. Familial hypercholesterolemia. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The Metabolic & Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001. pp. 2863–2913.
-
- Austin MA, Hutter CM, Zimmern RL, Humphries SE. Genetic causes of monogenic heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: a HuGE prevalence review. Am J Epidemiol. 2004;160:407–420. - PubMed
-
- Marks D, Thorogood M, Neil HA, Humphries SE. A review on the diagnosis, natural history, and treatment of familial hypercholesterolaemia. Atherosclerosis. 2003;168:1–14. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. World Healths Statistics 2012. Internet http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2012/en/ 9 October 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

