Suppression of natural killer cell cytotoxicity in postpartum women: time course and potential mechanisms
- PMID: 23956351
- PMCID: PMC3925467
- DOI: 10.1177/1099800413498927
Suppression of natural killer cell cytotoxicity in postpartum women: time course and potential mechanisms
Abstract
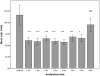
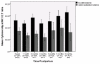
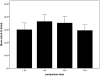
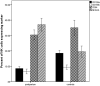
Little is known about the recovery of the immune system from normal pregnancy and whether the postpartum period is a uniquely adapted immune state. This report extends previous observations from our group of decreased natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxicity in the postpartum period. NK cytotoxicity was measured from 1 week through 9 months postpartum. In addition, NK cytotoxicity was assayed in the presence or absence of pooled plasmas collected from either postpartum or nonpostpartum women. Samples of cells were stained for inhibitory receptors and analyzed by flow cytometry. NK cytotoxicity remained decreased in postpartum women compared to controls through the first 6 postpartum months, returned to normal levels by 9 months, and remained normal at 12 months. NK cytotoxicity during the first 6 months was further inhibited by the addition of pooled plasma to NK cultures from postpartum women, but the addition of pooled plasma from the control group did not affect that group's NK cultures. There were differences in inhibitory receptor staining between the two groups, with decreased CD158a and CD158b and increased NKG2A expression on postpartum NK cells during the first 3 postpartum months. These data suggest that NK cytotoxicity postpartum inhibition lasts 6 months and is influenced by unidentified postpartum plasma components. The effect may also involve receptors on NK cells.
Keywords: NK cytotoxicity; flow cytometry; human leukocyte antigen-G; plasma effects; postpartum inhibition.
© The Author(s) 2013.
Figures
References
-
- Apps R, Gardner L, Moffett A. A critical look at HLA-G. Trends in Immunology. 2008;29:313–321. doi:10.1016/j.it.2008.02.012. - PubMed
-
- Borzychowski AM, Croy BA, Chan WL, Redman CW, Sargent IL. Changes in systemic type 1 and type 2 immunity in normal pregnancy and pre-eclampsia may be mediated by natural killer cells. European Journal of Immunology. 2005;35:3054–3063. doi:10.1002/eji.200425929. - PubMed
-
- Challis JR, Lockwood CJ, Myatt L, Norman JE, Strauss JF, Petraglia F. Inflammation and pregnancy. Reproductive Science. (3rd) 2009;16:206–215. doi:10.1177/1933719108329095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

