Comparison of the effects of remifentanil and alfentanil on intraocular pressure in cataract surgery
- PMID: 23956716
- PMCID: PMC3737692
- DOI: 10.4103/1658-354X.114074
Comparison of the effects of remifentanil and alfentanil on intraocular pressure in cataract surgery
Abstract
Background: Anesthesia for ophthalmic surgery requires management of intraocular pressure (IOP) during perioperative period. In an open eye, in conditions such as after traumatic injury or during cataract surgery, IOP increase can lead to permanent vision loss. Administration of narcotics concomitant with anesthetics has the ability to reduce this increase of IOP. This clinical trial aims to compare the efficacy of remifentanil and alfentanil in preventing an increase in IOP after administration of succinylcholine, intubation and during anesthesia.
Methods: This double-blind clinical trial was conducted on 50 patients undergoing elective general surgery for cataracts. Patients were randomly divided into two groups. Alfentanil (20 μg/kg in 30 s) for group 1 and remifentanil (1 μg/kg in 30 s) for group 2 were injected before induction of anesthesia, and 0.5 μg/kg/min alfentanil for group 1 and 0.1 μg/kg/min remifentanil for group 2 were infused during the anesthesia. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, and IOP from normal eye were measured before the induction, after administration of thiopental and succinylcholine, after tracheal intubation, and 2 min later, and were repeated in 2-min intervals until the end of operation.
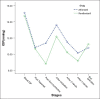
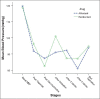
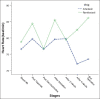
Results: IOP decreased after injection of anesthetics and remained lower all through the operation in both groups, but IOP decreased after injection of succinylcholine in remifentanil group while it increased in alfentanil group (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Results of this study indicate benefits of both remifentanil and alfentanil in managing IOP after induction and during anesthesia. It seems that remifentanil is better than alfentanil in controlling the IOP after injection of succinylcholine.
Keywords: Alfentanil; anesthesia; cataract surgery; intraocular pressure; remifentanil.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Short-Acting Opioids on Intraocular Pressure during General Anesthesia: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 11;15(8):989. doi: 10.3390/ph15080989. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of propofol and alfentanil on the increase in intraocular pressure due to succinylcholine and intubation.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2000 Apr-Jun;10(2):105-9. doi: 10.1177/112067210001000202. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 10887919 Clinical Trial.
-
Propofol and alfentanil prevent the increase in intraocular pressure caused by succinylcholine and endotracheal intubation during a rapid sequence induction of anesthesia.Anesth Analg. 1996 Oct;83(4):814-7. doi: 10.1097/00000539-199610000-00028. Anesth Analg. 1996. PMID: 8831327 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of remifentanil and remifentanil-alfentanil administration on emergence agitation after brief ophthalmic surgery in children.BMC Anesthesiol. 2016 Aug 2;16(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12871-016-0213-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2016. PMID: 27484339 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Fentanyl, Remifentanil, Sufentanil and Alfentanil in Combination with Propofol for General Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2019;14(2):116-124. doi: 10.2174/1567201816666190313160438. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30868958 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Short-Acting Opioids on Intraocular Pressure during General Anesthesia: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 11;15(8):989. doi: 10.3390/ph15080989. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examining the efficacy of intravenous ibuprofen and meperidine for preventing post-operative shivering after laparoscopic cholecystectomy with general anesthesia.J Med Life. 2023 Jul;16(7):1041-1046. doi: 10.25122/jml-2022-0040. J Med Life. 2023. PMID: 37900063 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of estrogen and progesterone therapy on intraocular pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis study.Eur J Transl Myol. 2025 Jun 27;35(2):13497. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2025.13497. Epub 2025 May 8. Eur J Transl Myol. 2025. PMID: 40341753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller RD. 6th ed. USA: Churchill Livingstone; 2005. Anesthesia; pp. 2351–3.
-
- Murgatroyd H, Bembridge J. Intraocular pressure. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2008;8:100–3. doi: 10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkn015.
-
- Alexander R, Hill R, Lipham WJ, Weatherwax KJ, el-Moalem HE. Remifentanil prevents an increase in intraocular pressure after succinylcholine and tracheal intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1998;81:606–7. - PubMed
-
- Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK. 4th ed. USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2001. Clinical Anesthesia; pp. 971–2.
-
- Akhavanakbari G, Entezariasl M, Pourfarzi F. Comparison of Remifentanil and Alfentanil Effects on the Hemodynamic Responses to Induction of Anesthesia and Tracheal Intubation in Elderly Patients. Res J Biol Sci. 2008;6:553–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

