Cellular Binding of Anionic Nanoparticles is Inhibited by Serum Proteins Independent of Nanoparticle Composition
- PMID: 23956836
- PMCID: PMC3743105
- DOI: 10.1039/C3BM60121H
Cellular Binding of Anionic Nanoparticles is Inhibited by Serum Proteins Independent of Nanoparticle Composition
Abstract
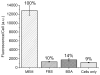
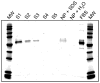
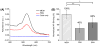
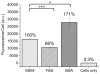
Nanoparticles used in biological applications encounter a complex mixture of extracellular proteins. Adsorption of these proteins on the nanoparticle surface results in the formation of a "protein corona," which can dominate the interaction of the nanoparticle with the cellular environment. The goal of this research was to determine how nanoparticle composition and surface modification affect the cellular binding of protein-nanoparticle complexes. We examined the cellular binding of a collection of commonly used anionic nanoparticles: quantum dots, colloidal gold nanoparticles, and low-density lipoprotein particles, in the presence and absence of extracellular proteins. These experiments have the advantage of comparing different nanoparticles under identical conditions. Using a combination of fluorescence and dark field microscopy, flow cytometry, and spectroscopy, we find that cellular binding of these anionic nanoparticles is inhibited by serum proteins independent of nanoparticle composition or surface modification. We expect these results will aid in the design of nanoparticles for in vivo applications.
Keywords: colloidal gold; nanoparticles; opsonization; protein corona; quantum dots; serum proteins.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle-cell interactions: molecular structure of the protein corona and cellular outcomes.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Aug 19;47(8):2651-9. doi: 10.1021/ar500190q. Epub 2014 Jul 11. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25014679 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle surface charge mediates the cellular receptors used by protein-nanoparticle complexes.J Phys Chem B. 2012 Aug 2;116(30):8901-7. doi: 10.1021/jp304630q. Epub 2012 Jul 20. J Phys Chem B. 2012. PMID: 22774860 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Corona in Response to Flow: Effect on Protein Concentration and Structure.Biophys J. 2018 Jul 17;115(2):209-216. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.02.036. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29650368 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle-Protein Interaction: The Significance and Role of Protein Corona.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1048:175-198. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-72041-8_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29453539 Review.
-
Interaction of nanoparticles with proteins: relation to bio-reactivity of the nanoparticle.J Nanobiotechnology. 2013 Jul 19;11:26. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-11-26. J Nanobiotechnology. 2013. PMID: 23870291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma protein corona modulates the vascular wall interaction of drug carriers in a material and donor specific manner.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 17;9(9):e107408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107408. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25229244 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Silica Nanoparticle Uptake into Human Osteoblast Cells by Variation of the Ratio of Amino and Sulfonate Surface Groups: Effects of Serum.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015 Jul 1;7(25):13821-33. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b01900. Epub 2015 Jun 21. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015. PMID: 26030456 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond the passive interactions at the nano-bio interface: evidence of Cu metalloprotein-driven oxidative dissolution of silver nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2016 Jan 22;14:7. doi: 10.1186/s12951-016-0160-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016. PMID: 26801765 Free PMC article.
-
Automation and low-cost proteomics for characterization of the protein corona: experimental methods for big data.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020 Sep;412(24):6543-6551. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02726-1. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32500258 Free PMC article.
-
The role of human serum and solution chemistry in fibrinogen peptide-nanoparticle interactions.Nanoscale Adv. 2020 Jun 1;2(6):2429-2440. doi: 10.1039/C9NA00793H. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Nanoscale Adv. 2020. PMID: 32864565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wagner V, Dullaart A, Bock AK, Zweck A. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1211–1217. - PubMed
-
- De M, Ghosh PS, Rotello VM. Adv Mater. 2008;20:4225–4241.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

