Sensory Response Patterns in Nonverbal Children with ASD
- PMID: 23956859
- PMCID: PMC3727194
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/436286
Sensory Response Patterns in Nonverbal Children with ASD
Abstract
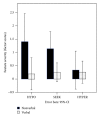
We sought to examine concurrent and longitudinal associations between sensory response patterns (i.e., hyperresponsiveness, hyporesponsiveness, and sensory seeking) and verbal status of young children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) as a potential factor influencing the development of verbal communication. Seventy-nine children with ASD (verbal, n = 29; nonverbal, n = 50) were assessed using cross-sectional analyses (Study 1), and 14 children with ASD (verbal, n = 6; nonverbal, n = 8) were assessed using prospective longitudinal analyses (Study 2). Data were collected regarding sensory response patterns and verbal ability. Hyporesponsiveness and sensory seeking behaviors were associated with verbal status in both cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses; nonverbal children were more likely to demonstrate higher hyporesponsive and sensory seeking patterns. Hyperresponsiveness did not significantly differ between verbal and nonverbal groups in either design. Sensory hyporesponsiveness and seeking behaviors may be important factors hindering the development of functional verbal communication in children with ASD. Unusual sensory responsiveness can often be observed before the onset of speech and may yield important prognostic capabilities as well as inform early interventions targeting verbal communication or alternative communication options in young children with ASD.
Figures
References
-
- Baghdadli A, Assouline B, Sonié S, et al. Developmental trajectories of adaptive behaviors from early childhood to adolescence in a cohort of 152 children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2012;42(7):1314–1325. - PubMed
-
- Lord C, Risi S, Pickles A. Trajectory of language development in autistic spectrum disorders. In: Rice ML, Warren SF, editors. Developmental Language Disorders: From Phenotypes to Etiologies. Mahwah, NJ, USA: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2004. pp. 7–29.
-
- Sigman M, McGovern CW. Improvement in cognitive and language skills from preschool to adolescence in autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2005;35(1):15–23. - PubMed
-
- Pickett E, Pullara O, O’Grady J, Gordon B. Speech acquisition in older nonverbal individuals with autism: a review of features, methods, and prognosis. Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology. 2009;22(1):1–21. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi R, Murata T, Yoshinaga K. A follow-up study of 201 children with autism in Kyushu and Yamaguchi areas, Japan. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 1992;22(3):395–411. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources