How effective is the local anesthetic infiltration of pin sites prior to application of head clamps: A prospective observational cohort study of hemodynamic response in patients undergoing elective craniotomy
- PMID: 23956936
- PMCID: PMC3740611
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.115237
How effective is the local anesthetic infiltration of pin sites prior to application of head clamps: A prospective observational cohort study of hemodynamic response in patients undergoing elective craniotomy
Abstract
Background: Use of Mayfield clamps is associated with potentially hazardous hemodynamic effects. Use of local anesthetic infiltration has yielded varying results in blunting of this response. The authors' objective was to study the effect of lidocaine with adrenaline infiltration at Mayfield pin sites on hemodynamic response in comparison with no intervention.
Methods: This was a prospective cohort study conducted at a tertiary care center from January 2012 to July 2012. Patents undergoing elective craniotomies over the study period were included and divided in two groups, Group A received lidocaine infiltration of the pin sites prior to insertion, while Group B did not. Hemodynamic response to pin application was then studied at various intervals.
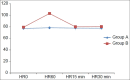
Results: A total of 30 patients were enrolled in each group. The baseline mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate prior to pin placement in Groups A and B were comparable (P = 0.985 and 0.313). The MAP at 60 seconds after application of skull pins was significantly different in the two groups; 86.13 (±9.73) mmHg versus 104.03 (±12.95) mmHg (P < 0.001). However, the MAP at 30 minutes after application of skull pins in both groups was comparable (P = 0.585). The mean heart rate measured at 60 seconds after skull pin insertion in Group A was 78.23 (±7.19)/min while in Group B, it was 103.07 (±6.98)/min, the difference being statistically significant (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Hemodynamic changes due to the application of Mayfield clamps during elective craniotomies can be effectively prevented by prior lidocaine with adrenaline infiltration of the pin insertion sites.
Keywords: Hemodynamics; Mayfield clamp; lidocaine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gabapentin premedication decreases the hemodynamic response to skull pin insertion in patients undergoing craniotomy.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2011 Apr;23(2):110-7. doi: 10.1097/ANA.0b013e3181da3c3b. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2011. PMID: 20479668 Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of alfentanil, esmolol, lidocaine, and thiopental sodium on the hemodynamic response to insertion of headrest skull pins.J Clin Anesth. 1996 Feb;8(1):31-5. doi: 10.1016/0952-8180(95)00169-7. J Clin Anesth. 1996. PMID: 8695076 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of a subanesthetic dose of intravenous ketamine and/or local anesthetic infiltration on hemodynamic responses to skull-pin placement: a prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2001 Jul;13(3):189-94. doi: 10.1097/00008506-200107000-00002. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2001. PMID: 11426091 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine on hemodynamic response in patients undergoing skull-pin head-holder application during neurosurgery - A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Aug;195:105939. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.105939. Epub 2020 May 20. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32480196
-
The Mayfield Skull Clamp: A Literature Review of Its Complications and Technical Nuances for Application.World Neurosurg. 2021 Jul;151:102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.04.081. Epub 2021 Apr 30. World Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33940273 Review.
Cited by
-
Analgesia nociception index and hemodynamic changes during skull pin application for supratentorial craniotomies in patients receiving scalp block versus pin-site infiltration: A randomized controlled trial.Saudi J Anaesth. 2019 Oct-Dec;13(4):306-311. doi: 10.4103/sja.SJA_812_18. Saudi J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31572074 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of intravenous labetalol and bupivacaine scalp block on the hemodynamic and entropy changes following skull pin application: A randomized, open label clinical trial.Asian J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan-Mar;11(1):60-5. doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.165801. Asian J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26889282 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Intranasal and Intravenous Dexmedetomidine on Hemodynamic Responses to Tracheal Intubation and Skull Pin Holder Fixation: A Double-Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial.Cureus. 2025 Jan 5;17(1):e76980. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76980. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39912047 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Intravenous Dexmedetomidine with Local Infiltration of Ropivacaine in Attenuation of Stress Response to Skull Pin Insertion in Craniotomies.Asian J Neurosurg. 2022 Oct 8;17(3):463-469. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1757221. eCollection 2022 Sep. Asian J Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 36398172 Free PMC article.
-
A novel temporary cranial fixation device for awake cranial surgery: Technical report of 14 cases.Surg Neurol Int. 2020 Jan 24;11:12. doi: 10.25259/SNI_442_2019. eCollection 2020. Surg Neurol Int. 2020. PMID: 32038884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal A, Sinha PK, Pandey CM, Gaur A, Pandey CK, Kaushik S. Effect of a subanesthetic dose of intravenous ketamine and/or local anesthetic infiltration on hemodynamic responses to skull-pin placement: A prospective, placebo-controlled, randomized, double-blind study. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2001;13:189–94. - PubMed
-
- Bayer-Berger MM, Ravussin P, Fankhauser H, Freeman J. Effect of three pretreatment techniques on hemodynamic and CSFP responses to skull-pin head-holder application during thiopentone/isoflurane or propofol anesthesia. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 1989;1:227–32. - PubMed
-
- Bithal PK, Pandia MP, Chouhan RS, Sharma D, Bhagat H, Dash HH, et al. Hemodynamic and bispectral index changes following skull pin attachment with and without local anesthetic infiltration of the scalp. J Anesth. 2007;21:442–4. - PubMed
-
- Bloomfield EL, Schubert A, Secic M, Barnett G, Shutway F, Ebrahim ZY. The influence of scalp infiltration with bupivacaine on hemodynamics and postoperative pain in adult patients undergoing craniotomy. Anesth Analg. 1998;87:579–82. - PubMed
-
- Doblar DD, Lim YC, Baykan N, Frenette L. A comparison of alfentanil, esmolol, lidocaine, and thiopental sodium on the hemodynamic response to insertion of headrest skull pins. J Clin Anesth. 1996;8:31–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

