Depletion of the cellular antioxidant system contributes to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate - induced mitochondrial damage and increased oxido-nitrosative stress in the kidney
- PMID: 23957306
- PMCID: PMC3765371
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-61
Depletion of the cellular antioxidant system contributes to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate - induced mitochondrial damage and increased oxido-nitrosative stress in the kidney
Abstract
Background: Nephrotoxicity is a dose limiting side effect of tenofovir, a reverse transcriptase inhibitor that is used for the treatment of HIV infection. The mechanism of tenofovir nephrotoxicity is not clear. Tenofovir is specifically toxic to the proximal convoluted tubules and proximal tubular mitochondria are the targets of tenofovir cytotoxicity. Damaged mitochondria are major sources of reactive oxygen species and cellular damage is reported to occur after the antioxidants are depleted. The purpose of the study is to investigate the alterations in cellular antioxidant system in tenofovir induced renal damage using a rat model.
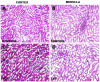
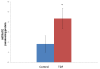
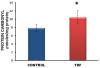
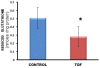
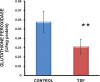
Results: Chronic tenofovir administration to adult Wistar rats resulted in proximal tubular damage (as evidenced by light microscopy), proximal tubular dysfunction (as shown by Fanconi syndrome and tubular proteinuria), and extensive proximal tubular mitochondrial injury (as revealed by electron microscopy). A 50% increase in protein carbonyl content was observed in the kidneys of TDF treated rats as compared with the control. Reduced glutathione was decreased by 50%. The activity of superoxide dismutase was decreased by 57%, glutathione peroxidase by 45%, and glutathione reductase by 150% as compared with control. Carbonic Anhydrase activity was decreased by 45% in the TDF treated rat kidneys as compared with control. Succinate dehydrogenase activity, an indicator of mitochondrial activity was decreased by 29% in the TDF treated rat kidneys as compared with controls, suggesting mitochondrial dysfunction.
Conclusion: Tenofovir- induced mitochondrial damage and increased oxidative stress in the rat kidneys may be due to depletion of the antioxidant system particularly, the glutathione dependent system and MnSOD.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and electron transport chain complex defect in a rat model of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate nephrotoxicity.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2014 Jun;28(6):246-55. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21560. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24615786
-
Mitochondrial tubulopathy in tenofovir disoproxil fumarate-treated rats.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009 Jul 1;51(3):258-63. doi: 10.1097/qai.0b013e3181a666eb. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009. PMID: 19582894
-
Tenofovir renal proximal tubular toxicity is regulated by OAT1 and MRP4 transporters.Lab Invest. 2011 Jun;91(6):852-8. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.48. Epub 2011 Mar 14. Lab Invest. 2011. PMID: 21403643 Free PMC article.
-
Tenofovir-induced nephrotoxicity: incidence, mechanism, risk factors, prognosis and proposed agents for prevention.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014 Sep;70(9):1029-40. doi: 10.1007/s00228-014-1712-z. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24958564 Review.
-
Proximal tubular renal dysfunction or damage in HIV-infected patients.AIDS Rev. 2012 Jul-Sep;14(3):179-87. AIDS Rev. 2012. PMID: 22833061 Review.
Cited by
-
Higher tenofovir exposure is associated with longitudinal declines in kidney function in women living with HIV.AIDS. 2016 Feb 20;30(4):609-18. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000958. AIDS. 2016. PMID: 26558723 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate on Bone Quality beyond Bone Density-A Scoping Review of the Literature.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;17(2):146. doi: 10.3390/ph17020146. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399361 Free PMC article.
-
Combination ART-Induced Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress, Neurogenic Inflammation and Cardiac Dysfunction in HIV-1 Transgenic (Tg) Rats: Protection by Mg.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 15;19(8):2409. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082409. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30111743 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of High-Throughput Imaging and Multiparametric Metabolic Profiling Reveals a Mitochondrial Mechanism of Tenofovir Toxicity.Function (Oxf). 2022 Dec 24;4(1):zqac065. doi: 10.1093/function/zqac065. eCollection 2023. Function (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 36654930 Free PMC article.
-
Moringa oleifera Lam Leaf Extract Stimulates NRF2 and Attenuates ARV-Induced Toxicity in Human Liver Cells (HepG2).Plants (Basel). 2023 Apr 3;12(7):1541. doi: 10.3390/plants12071541. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050167 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA report: background package for NDA 21-356: VIREAD (tenofovir disoxoproxil fumarate) 2001. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/cder/approval/v.htm.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

