Tobacco in the Arab world: old and new epidemics amidst policy paralysis
- PMID: 23958628
- PMCID: PMC4153301
- DOI: 10.1093/heapol/czt055
Tobacco in the Arab world: old and new epidemics amidst policy paralysis
Abstract
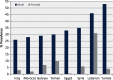
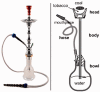
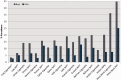
The Arab world is comprised of 22 countries with a combined population of ∼360 million. The region is still at the initial stages of the tobacco epidemic, where it is expected to witness an increase in smoking levels and mounting tobacco-related morbidity and mortality in the future. Still, the bleak outlook of the tobacco epidemic in the Arab world continues to be faced with complacency in the form of underutilization of surveillance systems to monitor the tobacco epidemic and prioritize action, and failure to implement and enforce effective policies to curb the tobacco epidemic. Understandably, the focus on the Arab world carries the risk of trying to generalize to such a diverse group of countries at different level of economic and political development. Yet, tobacco control in the Arab world faces some shared patterns and common challenges that need to be addressed to advance its cause in this region. In addition, forces that promote tobacco use, such as the tobacco industry, and trends in tobacco use, such as the emerging waterpipe epidemic tend to coalesce around some shared cultural and socio-political features of this region. Generally, available data from Arab countries point at three major trends in the tobacco epidemic: (1) high prevalence of cigarette smoking among Arab men compared with women; (2) the re-emergence of waterpipe (also known as hookah, narghile, shisha, arghile) smoking as a major tobacco use method, especially among youth and (3) the failure of policy to provide an adequate response to the tobacco epidemic. In this review, we will discuss these trends, factors contributing to them, and the way forward for tobacco control in this unstable region.
Keywords: Arab world; hookah; policy; tobacco industry; waterpipe.
Published by Oxford University Press in association with The London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine © The Author 2013; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akl EA, Gaddam S, Gunukula SK, et al. The effects of waterpipe tobacco smoking on health outcomes: a systematic review. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2010;39:834–57. - PubMed
-
- Alesci NL, Forster JL, Blaine T. Smoking visibility, perceived acceptability, and frequency in various locations among youth and adults. Preventive Medicine. 2003;36:272–81. - PubMed
-
- Ali AYM, Safwat T, Onyemelukwe G, et al. Smoking prevention and cessation in the Africa and Middle East region: a consensus draft guideline for healthcare providers—executive summary Respiration. International Review of Thoracic Diseases. 2012;83:423–32. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mulla AM, Abdou Helmy S, Al-Lawati J, et al. Prevalence of tobacco use among students aged 13-15 years in Health Ministers’ Council/Gulf Cooperation Council Member States, 2001-2004. Journal of School Health. 2008;78:337–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

