Kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin act in the arcuate nucleus to control activity of the GnRH pulse generator in ewes
- PMID: 23959940
- PMCID: PMC3800763
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2013-1331
Kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin act in the arcuate nucleus to control activity of the GnRH pulse generator in ewes
Abstract
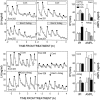
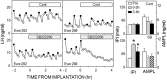
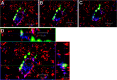
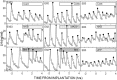
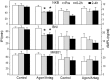
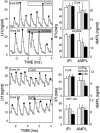
Recent work has led to the hypothesis that kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons in the arcuate nucleus play a key role in GnRH pulse generation, with kisspeptin driving GnRH release and neurokinin B (NKB) and dynorphin acting as start and stop signals, respectively. In this study, we tested this hypothesis by determining the actions, if any, of four neurotransmitters found in KNDy neurons (kisspeptin, NKB, dynorphin, and glutamate) on episodic LH secretion using local administration of agonists and antagonists to receptors for these transmitters in ovariectomized ewes. We also obtained evidence that GnRH-containing afferents contact KNDy neurons, so we tested the role of two components of these afferents: GnRH and orphanin-FQ. Microimplants of a Kiss1r antagonist briefly inhibited LH pulses and microinjections of 2 nmol of this antagonist produced a modest transitory decrease in LH pulse frequency. An antagonist to the NKB receptor also decreased LH pulse frequency, whereas NKB and an antagonist to the receptor for dynorphin both increased pulse frequency. In contrast, antagonists to GnRH receptors, orphanin-FQ receptors, and the N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor had no effect on episodic LH secretion. We thus conclude that the KNDy neuropeptides act in the arcuate nucleus to control episodic GnRH secretion in the ewe, but afferent input from GnRH neurons to this area does not. These data support the proposed roles for NKB and dynorphin within the KNDy neural network and raise the possibility that kisspeptin contributes to the control of GnRH pulse frequency in addition to its established role as an output signal from KNDy neurons that drives GnRH pulses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of arcuate neurons coexpressing kisspeptin, neurokinin B, and dynorphin by modulators of neurokinin 3 and κ-opioid receptors in adult male mice.Endocrinology. 2013 Aug;154(8):2761-71. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1268. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23744642 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of the GnRH pulse generator by neurokinin B involves a κ-opioid receptor-dependent mechanism.Endocrinology. 2012 Oct;153(10):4894-904. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1574. Epub 2012 Aug 17. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22903614
-
Lesions of KNDy and Kiss1R Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus Produce Different Effects on LH Pulse Patterns in Female Sheep.Endocrinology. 2023 Sep 23;164(11):bqad148. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad148. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37776515 Free PMC article.
-
A role for neurokinin B in pulsatile GnRH secretion in the ewe.Neuroendocrinology. 2014;99(1):18-32. doi: 10.1159/000355285. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Neuroendocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24008670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Roles of Neurokinins and Endogenous Opioid Peptides in Control of Pulsatile LH Secretion.Vitam Horm. 2018;107:89-135. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2018.01.011. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Vitam Horm. 2018. PMID: 29544644 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphological and functional evidence for sexual dimorphism in neurokinin B signalling in the retrochiasmatic area of sheep.J Neuroendocrinol. 2020 Jul;32(7):e12877. doi: 10.1111/jne.12877. Epub 2020 Jun 22. J Neuroendocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32572994 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism underlying the pubertal increase in pulsatile GnRH release in primates.J Neuroendocrinol. 2022 May;34(5):e13119. doi: 10.1111/jne.13119. Epub 2022 May 1. J Neuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35491543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypothalamic molecular changes underlying natural reproductive senescence in the female rat.Endocrinology. 2014 Sep;155(9):3597-609. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1017. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Endocrinology. 2014. PMID: 24914937 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Season and Estradiol on KNDy Neuron Peptides, Colocalization With D2 Dopamine Receptors, and Dopaminergic Inputs in the Ewe.Endocrinology. 2017 Apr 1;158(4):831-841. doi: 10.1210/en.2016-1830. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28324006 Free PMC article.
-
17β-Estradiol Increases Arcuate KNDy Neuronal Sensitivity to Ghrelin Inhibition of the M-Current in Female Mice.Neuroendocrinology. 2020;110(7-8):582-594. doi: 10.1159/000503146. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Neuroendocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31484184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karsch FJ. Central actions of ovarian steroids in the feedback regulation of pulsatile secretion of luteinizing hormone. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:365–382 - PubMed
-
- Belchetz PE, Plant TM, Nakai Y, Keogh EJ, Knobil E. Hypophysial responses to continuous and intermittent delivery of hypopthalamic gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Science. 1978;202:631–633 - PubMed
-
- Moenter SM, DeFazio AR, Pitts GR, Nunemaker CS. Mechanisms underlying episodic gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2003;24:79–93 - PubMed
-
- Terasawa E. Cellular mechanism of pulsatile LHRH release. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1998;112:283–295 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

