The role of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae lipoate protein ligase homologue, Lip3, in lipoic acid synthesis
- PMID: 23960015
- PMCID: PMC3806487
- DOI: 10.1002/yea.2979
The role of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae lipoate protein ligase homologue, Lip3, in lipoic acid synthesis
Abstract
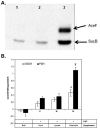
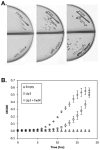
The covalent attachment of lipoate to the lipoyl domains (LDs) of the central metabolism enzymes pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and oxoglutarate dehydrogenase (OGDH) is essential for their activation and thus for respiratory growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A third lipoate-dependent enzyme system, the glycine cleavage system (GCV), is required for utilization of glycine as a nitrogen source. Lipoate is synthesized by extraction of its precursor, octanoyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP), from the pool of fatty acid biosynthetic intermediates. Alternatively, lipoate is salvaged from previously modified proteins or from growth medium by lipoate protein ligases (Lpls). The first Lpl to be characterized, LplA of Escherichia coli, catalyses two partial reactions: activation of the acyl chain by formation of acyl-AMP, followed by transfer of the acyl chain to lipoyl domains (LDs). There is a surprising diversity within the Lpl family of enzymes, several of which catalyse reactions other than ligation reactions. For example, the Bacillus subtilis Lpl homologue LipM is an octanoyltransferase that transfers the octanoyl moiety from octanoyl-ACP to GCV. Another B. subtilis Lpl homologue, LipL, transfers octanoate from octanoyl-GCV to other LDs in an amido-transfer reaction. Study of eukaryotic Lpls has lagged behind studies of the bacterial enzymes. We report that the Lip3 Lpl homologue of the yeast S. cerevisiae has octanoyl-CoA-protein transferase activity, and discuss implications of this activity on the physiological role of Lip3 in lipoate synthesis.
Keywords: lipoate protein ligase; lipoic acid; mitochondrial integrity; octanoyl-CoA; protein transferase; respiration; tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Published 2013. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Lipoic acid attachment to proteins: stimulating new developments.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Jun 27;88(2):e0000524. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00005-24. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38624243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipoic acid synthesis: a new family of octanoyltransferases generally annotated as lipoate protein ligases.Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 23;49(46):10024-36. doi: 10.1021/bi101215f. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Biochemistry. 2010. PMID: 20882995 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid metabolism in Escherichia coli: the lplA and lipB genes define redundant pathways for ligation of lipoyl groups to apoprotein.J Bacteriol. 1995 Jan;177(1):1-10. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.1-10.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 8002607 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoate protein ligase B primarily recognizes the C8-phosphopantetheine arm of its donor substrate and weakly binds the acyl carrier protein.J Biol Chem. 2022 Aug;298(8):102203. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102203. Epub 2022 Jun 25. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35764173 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014 Jul;37(4):553-63. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9705-8. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014. PMID: 24777537 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation.J Biol Chem. 2018 May 18;293(20):7522-7530. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM117.000259. Epub 2017 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29191830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MECR Mutations Cause Childhood-Onset Dystonia and Optic Atrophy, a Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Synthesis Disorder.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 Dec 1;99(6):1229-1244. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.09.021. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27817865 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering acetyl coenzyme A supply: functional expression of a bacterial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the cytosol of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.mBio. 2014 Oct 21;5(5):e01696-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01696-14. mBio. 2014. PMID: 25336454 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoic acid attachment to proteins: stimulating new developments.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Jun 27;88(2):e0000524. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00005-24. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38624243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly of Lipoic Acid on Its Cognate Enzymes: an Extraordinary and Essential Biosynthetic Pathway.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Apr 13;80(2):429-50. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00073-15. Print 2016 Jun. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27074917 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen XJ. Cloning and characterization of the lipoyl-protein ligase gene LIPB from the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis: synergistic respiratory deficiency due to mutations in LIPB and mitochondrial F1-ATPase subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1997;255:341–349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
