FRAX597, a small molecule inhibitor of the p21-activated kinases, inhibits tumorigenesis of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-associated Schwannomas
- PMID: 23960073
- PMCID: PMC3790009
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.510933
FRAX597, a small molecule inhibitor of the p21-activated kinases, inhibits tumorigenesis of neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)-associated Schwannomas
Abstract
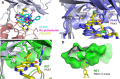
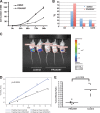
The p21-activated kinases (PAKs) are immediate downstream effectors of the Rac/Cdc42 small G-proteins and implicated in promoting tumorigenesis in various types of cancer including breast and lung carcinomas. Recent studies have established a requirement for the PAKs in the pathogenesis of Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), a dominantly inherited cancer disorder caused by mutations at the NF2 gene locus. Merlin, the protein product of the NF2 gene, has been shown to negatively regulate signaling through the PAKs and the tumor suppressive functions of Merlin are mediated, at least in part, through inhibition of the PAKs. Knockdown of PAK1 and PAK2 expression, through RNAi-based approaches, impairs the proliferation of NF2-null schwannoma cells in culture and inhibits their ability to form tumors in vivo. These data implicate the PAKs as potential therapeutic targets. High-throughput screening of a library of small molecules combined with a structure-activity relationship approach resulted in the identification of FRAX597, a small-molecule pyridopyrimidinone, as a potent inhibitor of the group I PAKs. Crystallographic characterization of the FRAX597/PAK1 complex identifies a phenyl ring that traverses the gatekeeper residue and positions the thiazole in the back cavity of the ATP binding site, a site rarely targeted by kinase inhibitors. FRAX597 inhibits the proliferation of NF2-deficient schwannoma cells in culture and displayed potent anti-tumor activity in vivo, impairing schwannoma development in an orthotopic model of NF2. These studies identify a novel class of orally available ATP-competitive Group I PAK inhibitors with significant potential for the treatment of NF2 and other cancers.
Keywords: Enzyme Inhibitors; Merlin; Protein Kinases; Schwann Cells; Signal Transduction; Small Molecules; nf2; p21-activated Kinase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Validation of the p21-activated kinases as targets for inhibition in neurofibromatosis type 2.Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 1;68(19):7932-7. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0866. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18829550 Free PMC article.
-
PAK1 inhibition reduces tumor size and extends the lifespan of mice in a genetically engineered mouse model of Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2).Hum Mol Genet. 2021 Aug 12;30(17):1607-1617. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab106. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. PMID: 34075397 Free PMC article.
-
LIM domain kinases as potential therapeutic targets for neurofibromatosis type 2.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 3;33(27):3571-82. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.320. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23934191 Free PMC article.
-
Development of small-molecule inhibitors of the group I p21-activated kinases, emerging therapeutic targets in cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Sep 1;80(5):683-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.03.012. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20302846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the p21-Activated Kinase Family in Tumor Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 20;26(8):3885. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083885. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332759 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel pipeline for prioritizing cancer type-specific therapeutic vulnerabilities using DepMap identifies PAK2 as a target in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.Mol Oncol. 2024 Feb;18(2):336-349. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13558. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37997254 Free PMC article.
-
Rac GTPases in Hematological Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 14;19(12):4041. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124041. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30558116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of Rho GTPases in Human Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 7;12(5):1179. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051179. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32392742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prenylated quinolinecarboxylic acid compound-18 prevents sensory nerve fiber outgrowth through inhibition of the interleukin-31 pathway.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 4;16(2):e0246630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246630. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33539470 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Vascular Injury and Repair by P21-Activated Kinase 1 and P21-Activated Kinase 2: Therapeutic Potential and Challenges.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 13;14(12):1596. doi: 10.3390/biom14121596. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766303 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. (1992) The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 70, 401–410 - PubMed
-
- Nobes C. D., Hall A. (1995) Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81, 53–62 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

