Multiple ligands of von Willebrand factor-binding protein (vWbp) promote Staphylococcus aureus clot formation in human plasma
- PMID: 23960083
- PMCID: PMC3784736
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.493122
Multiple ligands of von Willebrand factor-binding protein (vWbp) promote Staphylococcus aureus clot formation in human plasma
Abstract
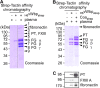
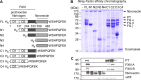
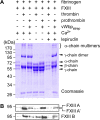
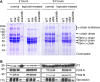
Staphylococcus aureus secretes coagulase (Coa) and von Willebrand factor-binding protein (vWbp) to activate host prothrombin and form fibrin cables, thereby promoting the establishment of infectious lesions. The D1-D2 domains of Coa and vWbp associate with, and non-proteolytically activate prothrombin. Moreover, Coa encompasses C-terminal tandem repeats for binding to fibrinogen, whereas vWbp has been reported to associate with von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen. Here we used affinity chromatography with non-catalytic Coa and vWbp to identify the ligands for these virulence factors in human plasma. vWbp bound to prothrombin, fibrinogen, fibronectin, and factor XIII, whereas Coa co-purified with prothrombin and fibrinogen. vWbp association with fibrinogen and factor XIII, but not fibronectin, required prothrombin and triggered the non-proteolytic activation of FXIII in vitro. Staphylococcus aureus coagulation of human plasma was associated with the recruitment of prothrombin, FXIII, and fibronectin as well as the formation of cross-linked fibrin. FXIII activity in staphylococcal clots could be attributed to thrombin-dependent proteolytic activation as well as vWbp-mediated non-proteolytic activation of FXIII zymogen.
Keywords: Coagulase; Coagulation Factors; Factor XIII; Fibrin; Fibrinogen; Fibronectin; Staphylococcus aureus; vWbp.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Complex Fibrinogen Interactions of the Staphylococcus aureus Coagulases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 16;9:106. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00106. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31041195 Free PMC article.
-
von Willebrand factor-binding protein (vWbp)-activated factor XIII and transglutaminase 2 (TG2) promote cross-linking between FnBPA from Staphylococcus aureus and fibrinogen.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 19;13(1):11683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38972-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37468579 Free PMC article.
-
vhp Is a Fibrinogen-Binding Protein Related to vWbp in Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0116721. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01167-21. Epub 2021 Aug 3. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34340548 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus secretes coagulase and von Willebrand factor binding protein to modify the coagulation cascade and establish host infections.J Innate Immun. 2012;4(2):141-8. doi: 10.1159/000333447. Epub 2012 Jan 3. J Innate Immun. 2012. PMID: 22222316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus, master manipulator of the human hemostatic system.J Thromb Haemost. 2018 Mar;16(3):441-454. doi: 10.1111/jth.13928. Epub 2018 Jan 29. J Thromb Haemost. 2018. PMID: 29251820 Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cell-derived factor XIIIA contributes to sexual dimorphic defense against group B streptococcal infections.J Clin Invest. 2022 Oct 17;132(20):e157999. doi: 10.1172/JCI157999. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 36006736 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to the vessel wall under flow is mediated by von Willebrand factor-binding protein.Blood. 2014 Sep 4;124(10):1669-76. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-02-558890. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24951431 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the maintenance of disease-associated variation at the blood group-related gene B4galnt2 in house mice.BMC Evol Biol. 2017 Aug 14;17(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s12862-017-1035-7. BMC Evol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28806915 Free PMC article.
-
Evasion and interactions of the humoral innate immune response in pathogen invasion, autoimmune disease, and cancer.Clin Immunol. 2015 Oct;160(2):244-54. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.06.012. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26145788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Action of Staphylococcus aureus α-Toxin on Platelets and Myeloid Lineage Cells Contributes to Lethal Sepsis.Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Jun 10;17(6):775-87. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.05.011. Cell Host Microbe. 2015. PMID: 26067604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowy F. D. (1998) Staphylococcus aureus infections. New Engl. J. Med. 339, 520–532 - PubMed
-
- Klevens R. M., Morrison M. A., Nadle J., Petit S., Gershman K., Ray S., Harrison L. H., Lynfield R., Dumyati G., Townes J. M., Craig A. S., Zell E. R., Fosheim G. E., McDougal L. K., Carey R. B., Fridkin S. K. (2007) Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. JAMA 298, 1763–1771 - PubMed
-
- Bamberger D. M., Boyd S. E. (2005) Management of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Am. Fam. Physician 72, 2474–2481 - PubMed
-
- Weems J. J., Jr. (2001) The many faces of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Recognizing and managing its life-threatening manifestations. Postgrad. Med. 110, 24–26 - PubMed
-
- Grundmann H., Aires-de-Sousa M., Boyce J., Tiemersma E. (2006) Emergence and resurgence of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a public-health threat. Lancet 368, 874–885 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

