Berbamine inhibits the growth of liver cancer cells and cancer-initiating cells by targeting Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
- PMID: 23960096
- PMCID: PMC3808882
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-0314
Berbamine inhibits the growth of liver cancer cells and cancer-initiating cells by targeting Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
Abstract
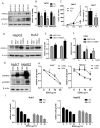
Liver cancer is the third leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide but no effective treatment toward liver cancer is available so far. Therefore, there is an unmet medical need to identify novel therapies to efficiently treat liver cancer and improve the prognosis of this disease. Here, we report that berbamine and one of its derivatives, bbd24, potently suppressed liver cancer cell proliferation and induced cancer cell death by targeting Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CAMKII). Furthermore, berbamine inhibited the in vivo tumorigenicity of liver cancer cells in NOD/SCID mice and downregulated the self-renewal abilities of liver cancer-initiating cells. Chemical inhibition or short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of CAMKII recapitulated the effects of berbamine, whereas overexpression of CAMKII promoted cancer cell proliferation and increased the resistance of liver cancer cells to berbamine treatments. Western blot analyses of human liver cancer specimens showed that CAMKII was hyperphosphorylated in liver tumors compared with the paired peritumor tissues, which supports a role of CAMKII in promoting human liver cancer progression and the potential clinical use of berbamine for liver cancer therapies. Our data suggest that berbamine and its derivatives are promising agents to suppress liver cancer growth by targeting CAMKII. Mol Cancer Ther; 12(10); 2067-77. ©2013 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
CaMKII γ, a critical regulator of CML stem/progenitor cells, is a target of the natural product berbamine.Blood. 2012 Dec 6;120(24):4829-39. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-434894. Epub 2012 Oct 16. Blood. 2012. PMID: 23074277 Free PMC article.
-
Berbamine suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer partially via the inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2018 Jun 1;50(6):532-539. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmy036. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2018. PMID: 29701777
-
Novel synthetic tosyl chloride-berbamine regresses lethal MYC-positive leukemia by targeting CaMKIIγ/Myc axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109134. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109134. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31247466
-
Regulation of Cell-Signaling Pathways by Berbamine in Different Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 2;23(5):2758. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052758. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Ca2+-calmodulin stimulated protein kinase II in ischaemic stroke - A potential target for neuroprotective therapies.Neurochem Int. 2017 Jul;107:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.01.012. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Neurochem Int. 2017. PMID: 28153786 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo superior radiosensitizing effect of berbamine for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Nov 14;11:8117-8125. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S171212. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30532553 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of the c-Myc Protein by CAMKIIγ Promotes T Cell Lymphoma.Cancer Cell. 2017 Jul 10;32(1):115-128.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.06.001. Cancer Cell. 2017. PMID: 28697340 Free PMC article.
-
Berbamine (BBM), a Natural STAT3 Inhibitor, Synergistically Enhances the Antigrowth and Proapoptotic Effects of Sorafenib on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells.ACS Omega. 2020 Sep 18;5(38):24838-24847. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03527. eCollection 2020 Sep 29. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33015502 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Daruharidra (Berberis aristata) Based Biogenic Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles: Their Implementation as Antibacterial and Novel Therapeutic Agents against Human Breast and Ovarian Cancer.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(12):1617-1628. doi: 10.2174/0113892010244977231108043554. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39034838
-
Discovery of a New CaMKII-Targeted Synthetic Lethal Therapy against Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 4;14(5):1315. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051315. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Thomas MB, Zhu AX. Hepatocellular carcinoma: the need for progress. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:2892–9. - PubMed
-
- Kassahun WT, Fangmann J, Harms J, Hauss J, Bartels M. Liver resection and transplantation in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review. Experimental and clinical transplantation: official journal of the Middle East Society for Organ Transplantation. 2006;4:549–58. - PubMed
-
- Carr BI. Some new approaches to the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Seminars in oncology. 2012;39:369–73. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka S, Arii S. Molecular targeted therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Seminars in oncology. 2012;39:486–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

