The interdependent, overlapping, and differential roles of type I and II IFNs in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 23960239
- PMCID: PMC3779698
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300419
The interdependent, overlapping, and differential roles of type I and II IFNs in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
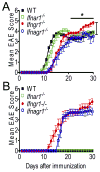
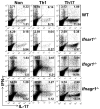
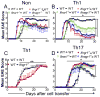
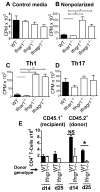
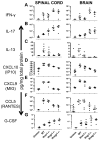
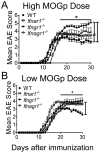
Type I IFNs (IFN-α and IFN-β) and type II IFN (IFN-γ) mediate both regulation and inflammation in multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, and in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). However, the underlying mechanism for these Janus-like activities of type I and II IFNs in neuroinflammation remains unclear. Although endogenous type I IFN signaling provides a protective response in neuroinflammation, we find that when IFN-γ signaling is ablated, type I IFNs drive inflammation, resulting in exacerbated EAE. IFN-γ has a disease stage-specific opposing function in EAE. Treatment of mice with IFN-γ during the initiation phase of EAE leads to enhanced severity of disease. In contrast, IFN-γ treatment during the effector phase attenuated disease. This immunosuppressive activity of IFN-γ required functional type I IFN signaling. In IFN-α/β receptor-deficient mice, IFN-γ treatment during effector phase of EAE exacerbated disease. Using an adoptive transfer EAE model, we found that T cell-intrinsic type I and II IFN signals are simultaneously required to establish chronic EAE by encephalitogenic Th1 cells. However, in Th17 cells loss of either IFN signals leads to the development of a severe chronic disease. The data imply that type I and II IFN signals have independent but nonredundant roles in restraining encephalitogenic Th17 cells in vivo. Collectively, our data show that type I and II IFNs function in an integrated manner to regulate pathogenesis in EAE.
Figures


References
-
- Farrar MA, Schreiber RD. The molecular cell biology of interferon-gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:571–611. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Baccala R, Beutler B, Kono DH. Type I interferons (alpha/beta) in immunity and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:307–336. - PubMed
-
- Pace JL. Synergistic interactions between IFN-gamma and IFN-beta in priming murine macrophages for tumor cell killing. J Leukoc Biol. 1988;44:514–520. - PubMed
-
- Dezfouli S, Hatzinisiriou I, Ralph SJ. Enhancing CTL responses to melanoma cell vaccines in vivo: synergistic increases obtained using IFNgamma primed and IFNbeta treated B7–1+ B16-F10 melanoma cells. Immunology and cell biology. 2003;81:459–471. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 NS047466/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS057098/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007051/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI1076562/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G20 RR02858/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR48311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR048311/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076562/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS064261/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS064261/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G20 RR022807/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G20 RR025858/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

