Urinary biomarkers for early detection of recovery in patients with acute kidney injury
- PMID: 23960445
- PMCID: PMC3744706
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.8.1181
Urinary biomarkers for early detection of recovery in patients with acute kidney injury
Abstract
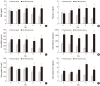
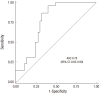
Urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury (AKI) have been revealed recently to be useful for prior prediction of AKI. However, it is unclear whether these urinary biomarkers can also detect recovery from established AKI. Urinary biomarkers, including neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and cystatin C, were measured every 2 days for 8 days in 66 patients with AKI. At day 0, there were no significant differences in plasma creatinine, BUN, and urine cystatin C between AKI patients in the recovery (n = 33) and non-recovery (n = 33) groups. Plasma creatinine concentrations were significantly lower in the recovery group (3.0 ± 2.0 mg/dL) than in the non-recovery group (5.4 ± 1.9 mg/dL) on day 4 after AKI diagnosis (P < 0.001). In contrast, there were significant differences in urine NGAL between the two groups starting on day 0 (297.2 ± 201.4 vs 407.6 ± 190.4 ng/mL, P = 0.025) through the end of the study (123.7 ± 119.0 vs 434.3 ± 121.5 ng/mL, P < 0.001). The multiple logistic regression analysis showed that urine NGAL could independently predict recovery from AKI. Conclusively, this prospective observational study demonstrates that urine NGAL can be a highly versatile marker for early detection of the recovery phase in established AKI patients.
Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury; Biological Markers; Cystatin C; Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin.
Figures
References
-
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1448–1460. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3365–3370. - PubMed
-
- Schrier RW. Early intervention in acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6:56–59. - PubMed
-
- Wald R, Quinn RR, Luo J, Li P, Scales DC, Mamdani MM, Ray JG University of Toronto Acute Kidney Injury Research Group. Chronic dialysis and death among survivors of acute kidney injury requiring dialysis. JAMA. 2009;302:1179–1185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

