Corticotomy facilitated orthodontics: Review of a technique
- PMID: 23960473
- PMCID: PMC3723293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2009.12.008
Corticotomy facilitated orthodontics: Review of a technique
Abstract
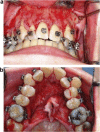
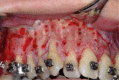
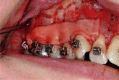
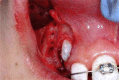
Corticotomy found to be effective in accelerating orthodontic treatment. The most important factors in the success of this technique is proper case selection and careful surgical and orthodontic treatment. Corticotomy facilitated orthodontics advocated for comprehensive fixed orthodontic appliances in conjunction with full thickness flaps and labial and lingual corticotomies around teeth to be moved. Bone graft should be applied directly over the bone cuts and the flap sutured in place. Tooth movement should be initiated two weeks after the surgery, and every two weeks thereafter by activation of the orthodontic appliance. Orthodontic treatment time with this technique will be reduced to one-third the time of conventional orthodontics. Alveolar augmentation of labial and lingual cortical plates were used in an effort to enhance and strengthen the periodontium, reasoning that the addition of bone to alveolar housing of the teeth, using modern bone grafting techniques, ensures root coverage as the dental arch expanded. Corticotomy facilitated orthodontics is promising procedure but only few cases were reported in the literature. Controlled clinical and histological studies are needed to understand the biology of tooth movement with this procedure, the effect on teeth and bone, post-retention stability, measuring the volume of mature bone formation, and determining the status of the periodontium and roots after treatment.
Keywords: Accelerated osteogenic orthodontics; Corticotomy facilitated orthodontics; Periodontally accelerated osteogenic orthodontics; Rapid orthodontics; Regional acceleratory phenomena.
Figures

References
-
- Duker J. Experimental animal research into segmental alveolar movement after corticotomy. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 1975;3:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Fischer T.J. Orthodontic treatment acceleration with corticotomy-assisted exposure of palatally impacted canines. Angle Orthod. 2007;77:417–420. - PubMed
-
- Frost H.M. The regional acceleratory phenomenon: a review. Henry Ford Hosp. Med. J. 1983;31:3–9. - PubMed
-
- Kole H. Surgical operations on the alveolar ridge to correct occlusal abnormalities. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1959;12:515–529. Concl. - PubMed
-
- Kole H. Surgical operations on the alveolar ridge to correct occlusal abnormalities. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1959;12:413–420. contd. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

