Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein modulates IRF-7-mediated interferon-α signaling
- PMID: 23962002
- PMCID: PMC3887440
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2013.0038
Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein modulates IRF-7-mediated interferon-α signaling
Abstract
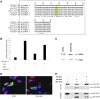
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) establishes chronic infection in a large number of infected individuals. We have previously shown that HCV infection in hepatocytes blocks poly (I-C) or interferon (IFN)-α-mediated IRF-7 nuclear translocation (Raychoudhuri and others 2010). However, the mechanism of IRF-7 regulation by HCV remained unknown. In this study, we have observed that HCV NS5A physically associates with IRF-7. A subsequent study suggested that the HCV NS5A protein blocks IRF-7-mediated IFN-α14 promoter activation. Further analyses demonstrated that site-specific mutagenesis of the 2 basic arginine residues (amino acids Arg(216) and Arg(217)) in the NS5A is critical for IRF-7-mediated IFN-α14 promoter regulation. Together, our results suggested that the HCV NS5A protein limits the IFN-α-signaling pathway in association with IRF-7, and may, in part, be responsible for the establishment of chronic infection.
Figures


References
-
- Aly HH, Watashi K, Hijikata M, Kaneko H, Takada Y, Egawa H, Uemoto S, Shimotohno K. 2007. Serum-derived hepatitis C virus infectivity in interferon regulatory factor-7-suppressed human primary hepatocytes. J Hepatol 46:26–36 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong GL, Wasley A, Simard EP, McQuillan GM, Kuhnert WL, Alter MJ. 2006. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann Intern Med 144:705–714 - PubMed
-
- Eddy SR. 1995. Multiple alignment using hidden Markov models. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 3:114–120 - PubMed
-
- Honda K, Yanai H, Negishi H, Asagiri M, Sato M, Mizutani T, Shimada N, Ohba Y, Takaoka A, Yoshida N, Taniguchi T. 2005. IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses. Nature 434:772–777 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

