Diversity of picoeukaryotes at an oligotrophic site off the Northeastern Red Sea Coast
- PMID: 23962380
- PMCID: PMC3766091
- DOI: 10.1186/2046-9063-9-16
Diversity of picoeukaryotes at an oligotrophic site off the Northeastern Red Sea Coast
Abstract
Background: Picoeukaryotes are protists ≤ 3 μm composed of a wide diversity of taxonomic groups. They are an important constituent of the ocean's microbiota and perform essential ecological roles in marine nutrient and carbon cycles. Despite their importance, the true extent of their diversity has only recently been uncovered by molecular surveys that resulted in the discovery of a substantial number of previously unknown groups. No study on picoeukaryote diversity has been conducted so far in the main Red Sea basin-a unique marine environment characterized by oligotrophic conditions, high levels of irradiance, high salinity and increased water temperature.
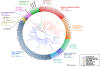
Results: We sampled surface waters off the coast of the northeastern Red Sea and analyzed the picoeukaryotic diversity using Sanger-based clone libraries of the 18S rRNA gene in order to produce high quality, nearly full-length sequences. The community captured by our approach was dominated by three main phyla, the alveolates, stramenopiles and chlorophytes; members of Radiolaria, Cercozoa and Haptophyta were also found, albeit in low abundances. Photosynthetic organisms were especially diverse and abundant in the sample, confirming the importance of picophytoplankton for primary production in the basin as well as indicating the existence of numerous ecological micro-niches for this trophic level in the upper euphotic zone. Heterotrophic organisms were mostly composed of the presumably parasitic Marine Alveolates (MALV) and the presumably bacterivorous Marine Stramenopiles (MAST) groups. A small number of sequences that did not cluster closely with known clades were also found, especially in the MALV-II group, some of which could potentially belong to novel clades.
Conclusions: This study provides the first snapshot of the picoeukaryotic diversity present in surface waters of the Red Sea, hence setting the stage for large-scale surveying and characterization of the eukaryotic diversity in the entire basin. Our results indicate that the picoeukaryotic community in the northern Red Sea, despite its unique physiochemical conditions (i.e. increased temperatures, increased salinity, and high UV irradiance) does not differ vastly from its counterparts in other oligotrophic marine habitats.
Figures
References
-
- Li WKW. Primary production of prochlorophytes, cyanobacteria, and eucaryotic ultraphytoplankton: measurements from flow cytometric sorting. Limnol Oceanogr. 1994;39:169–175. doi: 10.4319/lo.1994.39.1.0169. - DOI
-
- Biegala IC, Not F, Vaulot D, Simon N. Quantitative assessment of picoeukaryotes in the natural environment by using taxon-specific oligonucleotide probes in association with tyramide signal amplification fluorescence in situ hybridization and flow cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:5519–5529. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.9.5519-5529.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

